本文实例为大家分享了pytorch实现线性回归以及多元回归的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
最近在学习pytorch,现在把学习的代码放在这里,下面是github链接
直接附上github代码
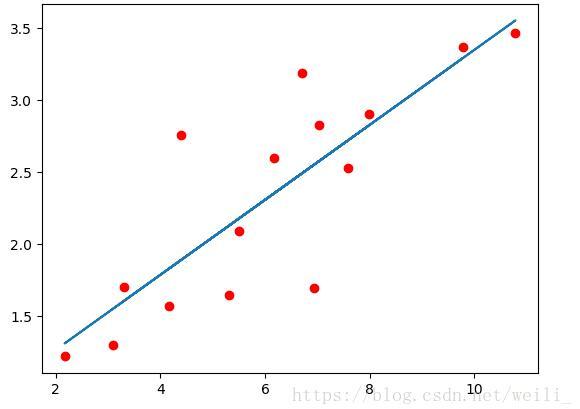
# 实现一个线性回归 # 所有的层结构和损失函数都来自于 torch.nn # torch.optim 是一个实现各种优化算法的包,调用的时候必须是需要优化的参数传入,这些参数都必须是Variable x_train = np.array([[3.3],[4.4],[5.5],[6.71],[6.93],[4.168],[9.779],[6.182],[7.59],[2.167],[7.042],[10.791],[5.313],[7.997],[3.1]],dtype=np.float32) y_train = np.array([[1.7],[2.76],[2.09],[3.19],[1.694],[1.573],[3.366],[2.596],[2.53],[1.221],[2.827],[3.465],[1.65],[2.904],[1.3]],dtype=np.float32) # 首先我们需要将array转化成tensor,因为pytorch处理的单元是Tensor x_train = torch.from_numpy(x_train) y_train = torch.from_numpy(y_train) # def a simple network class LinearRegression(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(LinearRegression,self).__init__() self.linear = nn.Linear(1, 1) # input and output is 2_dimension def forward(self, x): out = self.linear(x) return out if torch.cuda.is_available(): model = LinearRegression().cuda() #model = model.cuda() else: model = LinearRegression() #model = model.cuda() # 定义loss function 和 optimize func criterion = nn.MSELoss() # 均方误差作为优化函数 optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=1e-3) num_epochs = 30000 for epoch in range(num_epochs): if torch.cuda.is_available(): inputs = Variable(x_train).cuda() outputs = Variable(y_train).cuda() else: inputs = Variable(x_train) outputs = Variable(y_train) # forward out = model(inputs) loss = criterion(out,outputs) # backword optimizer.zero_grad() # 每次做反向传播之前都要进行归零梯度。不然梯度会累加在一起,造成不收敛的结果 loss.backward() optimizer.step() if (epoch +1)%20==0: print('Epoch[{}/{}], loss: {:.6f}'.format(epoch+1,num_epochs,loss.data)) model.eval() # 将模型变成测试模式 predict = model(Variable(x_train).cuda()) predict = predict.data.cpu().numpy() plt.plot(x_train.numpy(),y_train.numpy(),'ro',label = 'original data') plt.plot(x_train.numpy(),predict,label = 'Fitting line') plt.show()结果如图所示:
多元回归:
# _*_encoding=utf-8_*_ # pytorch 里面最基本的操作对象是Tensor,pytorch 的tensor可以和numpy的ndarray相互转化。 # 实现一个线性回归 # 所有的层结构和损失函数都来自于 torch.nn # torch.optim 是一个实现各种优化算法的包,调用的时候必须是需要优化的参数传入,这些参数都必须是Variable # 实现 y = b + w1 *x + w2 *x**2 +w3*x**3 import os os.environ['CUDA_DEVICE_ORDER']="PCI_BUS_ID" os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES']='0' import torch import numpy as np from torch.autograd import Variable import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from torch import nn # pre_processing def make_feature(x): x = x.unsqueeze(1) # unsquenze 是为了添加维度1的,0表示第一维度,1表示第二维度,将tensor大小由3变为(3,1) return torch.cat([x ** i for i in range(1, 4)], 1) # 定义好真实的数据 def f(x): W_output = torch.Tensor([0.5, 3, 2.4]).unsqueeze(1) b_output = torch.Tensor([0.9]) return x.mm(W_output)+b_output[0] # 外积,矩阵乘法 # 批量处理数据 def get_batch(batch_size =32): random = torch.randn(batch_size) x = make_feature(random) y = f(x) if torch.cuda.is_available(): return Variable(x).cuda(),Variable(y).cuda() else: return Variable(x),Variable(y) # def model class poly_model(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(poly_model,self).__init__() self.poly = nn.Linear(3,1) def forward(self,input): output = self.poly(input) return output if torch.cuda.is_available(): print("sdf") model = poly_model().cuda() else: model = poly_model() # 定义损失函数和优化器 criterion = nn.MSELoss() optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3) epoch = 0 while True: batch_x, batch_y = get_batch() #print(batch_x) output = model(batch_x) loss = criterion(output,batch_y) print_loss = loss.data optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() epoch = epoch +1 if print_loss < 1e-3: print(print_loss) break model.eval() print("Epoch = {}".format(epoch)) batch_x, batch_y = get_batch() predict = model(batch_x) a = predict - batch_y y = torch.sum(a) print('y = ',y) predict = predict.data.cpu().numpy() plt.plot(batch_x.cpu().numpy(),batch_y.cpu().numpy(),'ro',label = 'Original data') plt.plot(batch_x.cpu().numpy(),predict,'b', ls='--',label = 'Fitting line') plt.show()以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持python博客。
-
<< 上一篇 下一篇 >>
标签:numpy matplotlib
pytorch实现线性回归以及多元回归
看: 1570次 时间:2021-04-28 分类 : python教程
- 相关文章
- 2021-12-20Python 实现图片色彩转换案例
- 2021-12-20python初学定义函数
- 2021-12-20图文详解Python如何导入自己编写的py文件
- 2021-12-20python二分法查找实例代码
- 2021-12-20Pyinstaller打包工具的使用以及避坑
- 2021-12-20Facebook开源一站式服务python时序利器Kats详解
- 2021-12-20pyCaret效率倍增开源低代码的python机器学习工具
- 2021-12-20python机器学习使数据更鲜活的可视化工具Pandas_Alive
- 2021-12-20python读写文件with open的介绍
- 2021-12-20Python生成任意波形并存为txt的实现
-
搜索
-
-
推荐资源
-
Powered By python教程网 鲁ICP备18013710号
python博客 - 小白学python最友好的网站!