本文主要介绍了Pyecharts地理数据可视化,分享给大家,具体如下:
一、Pyecharts简介和安装
1. 简介
Echarts 是一个由百度开源的数据可视化,凭借着良好的交互性,精巧的图表设计,得到了众多开发者的认可。而 Python 是一门富有表达力的语言,很适合用于数据处理。当数据分析遇上数据可视化时,pyecharts 诞生了。
- 简洁的 API 设计,使用如丝滑般流畅,支持链式调用
- 囊括了 30+ 种常见图表,应有尽有
- 支持主流 Notebook 环境,Jupyter Notebook 和 JupyterLab
- 可轻松集成至 Flask,Sanic,Django 等主流 Web 框架
- 高度灵活的配置项,可轻松搭配出精美的图表
- 详细的文档和示例,帮助开发者更快的上手项目
- 多达 400+ 地图文件,并且支持原生百度地图,为地理数据可视化提供强有力的支持
pyecharts版本v0.5.x 和 v1 间不兼容,v1 是一个全新的版本,语法也有很大不同。
2. 安装
安装pyecharts
pip install pyecharts -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple --trusted-host pypi.douban.com``` ```python import pyecharts print(pyecharts.__version__) # 查看当前pyecharts版本``` <p>安装相关的地图扩展包</p> ```python pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple echarts-countries-pypkg # 全球国家地图 pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple echarts-china-provinces-pypkg # 中国省级地图 pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple echarts-china-cities-pypkg # 中国市级地图 pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple echarts-china-counties-pypkg # 中国县区级地图二、地图可视化
1. 世界地图
利用 Starbucks.csv 中的数据,首先计算每个国家(Country)对应的门店数量,然后使用世界地图可视化展示星巴克门面店在全球的数量分布。
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- """ @File :demo1.py @Author :叶庭云 @CSDN :https://yetingyun.blog.csdn.net/ """ import pandas as pd from pyecharts.charts import Map from pyecharts import options as opts from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType, CurrentConfig CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/' # pandas读取csv文件里的数据 df = pd.read_csv("Starbucks.csv")['Country'] # 统计各个地区星巴克门店数量 data = df.value_counts() datas = [(i, int(j)) for i, j in zip(data.index, data.values)] # 实例化一个Map对象 map_ = Map(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.PURPLE_PASSION)) # 世界地图 map_.add("门店数量", data_pair=datas, maptype="world") map_.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False)) # 不显示label map_.set_global_opts( title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="星巴克门店数量在全球分布", pos_left='40%', pos_top='10'), # 调整title位置 legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False), visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(max_=13608, min_=1, is_piecewise=True, pieces=[{"max": 9, "min": 1, "label": "1-9", "color": "#00FFFF"}, # 分段 添加图例注释和颜色 {"max": 99, "min": 10, "label": "10-99", "color": "#A52A2A"}, {"max": 499, "min": 100, "label": "100-499", "color": "#0000FF"}, {"max": 999, "min": 500, "label": "500-999", "color": "#FF00FF"}, {"max": 2000, "min": 1000, "label": "1000-2000", "color": "#228B22"}, {"max": 3000, "min": 2000, "label": "2000-3000", "color": "#FF0000"}, {"max": 20000, "min": 10000, "label": ">=10000", "color": "#FFD700"} ]) ) # 渲染在网页上 map_.render('星巴克门店在全球的分布.html')运行效果如下:

2. 国家地图
涟漪散点图
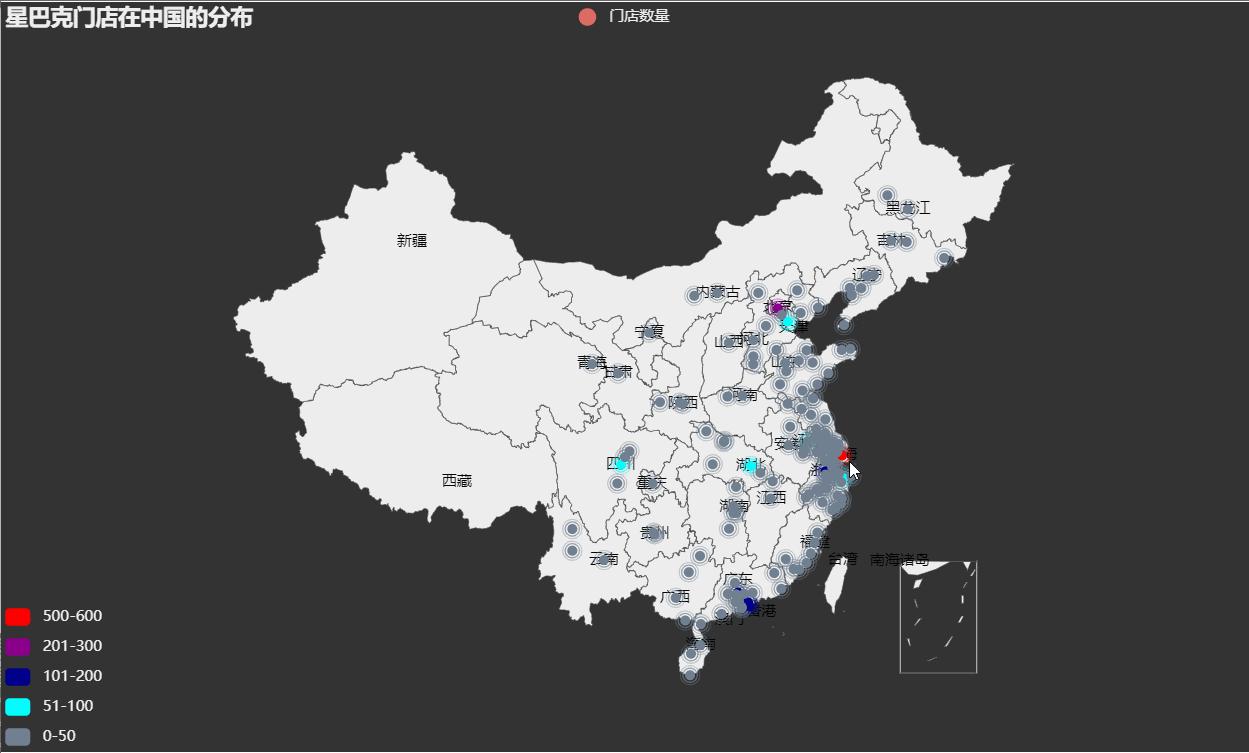
利用 china.csv 中的数据,首先计算每个城市(City)对应的门店数量,然后使用 pyecharts 包内 Geo 模块绘制星巴克门面店在中国各城市的数量分布的涟漪散点地图。
import pandas as pd from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType, CurrentConfig, GeoType from pyecharts import options as opts from pyecharts.charts import Geo CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/' # pandas读取csv文件数据 df = pd.read_csv("china.csv")['City'] data = df.value_counts() datas = [(i, int(j)) for i, j in zip(data.index, data.values)] print(datas) geo = Geo(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width='1000px', height='600px', theme=ThemeType.DARK)) geo.add_schema(maptype='china', label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True)) # 显示label 省名 geo.add('门店数量', data_pair=datas, type_=GeoType.EFFECT_SCATTER, symbol_size=8) geo.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False)) geo.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='星巴克门店在中国的分布'), visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(max_=550, is_piecewise=True, pieces=[{"max": 50, "min": 0, "label": "0-50", "color": "#708090"}, # 分段 添加图例注释 和颜色 {"max": 100, "min": 51, "label": "51-100", "color": "#00FFFF"}, {"max": 200, "min": 101, "label": "101-200", "color": "#00008B"}, {"max": 300, "min": 201, "label": "201-300", "color": "#8B008B"}, {"max": 600, "min": 500, "label": "500-600", "color": "#FF0000"}, ]) ) geo.render("星巴克门店在中国的分布.html")运行效果如下:
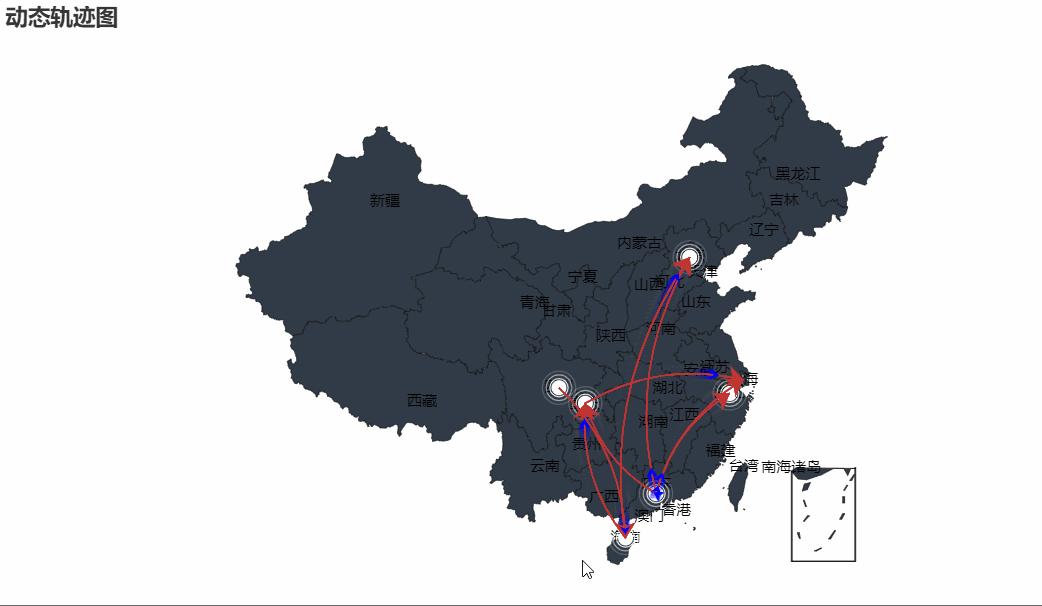
动态轨迹图
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- """ @File :demo3.py @Author :叶庭云 @CSDN :https://yetingyun.blog.csdn.net/ """ from pyecharts import options as opts from pyecharts.charts import Geo from pyecharts.globals import ChartType, SymbolType, CurrentConfig, ThemeType CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/' # 链式调用 c = ( Geo() .add_schema( maptype="china", itemstyle_opts=opts.ItemStyleOpts(color="#323c48", border_color="#111"), label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True) ) .add( "", [("广州", 55), ("北京", 66), ("杭州", 77), ("重庆", 88), ('成都', 100), ('海口', 80)], type_=ChartType.EFFECT_SCATTER, color="white", ) .add( "", [("广州", "上海"), ("广州", "北京"), ("广州", "杭州"), ("广州", "重庆"), ('成都', '海口'), ('海口', '北京'), ('海口', '重庆'), ('重庆', '上海') ], type_=ChartType.LINES, effect_opts=opts.EffectOpts( symbol=SymbolType.ARROW, symbol_size=6, color="blue" # 轨迹线蓝色 ), linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts(curve=0.2), # 轨迹线弯曲度 ) .set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False)) .set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="动态轨迹图")) .render("geo_lines_background.html") )运行效果如下:
3. 省市地图
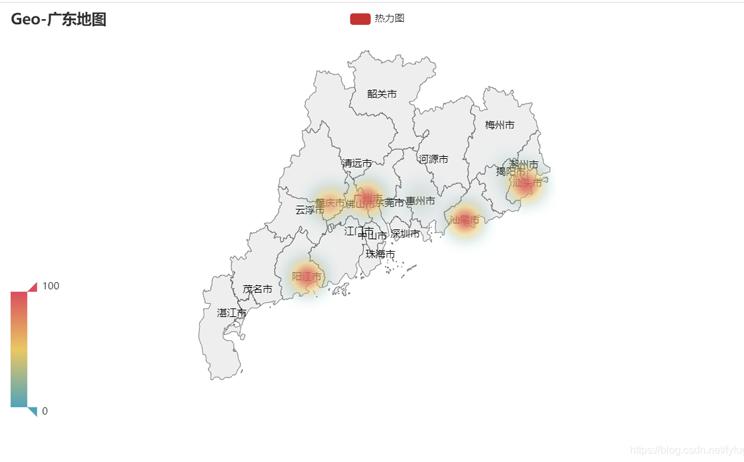
热力图
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- """ @File :demo4.py @Author :叶庭云 @CSDN :https://yetingyun.blog.csdn.net/ """ from pyecharts import options as opts from pyecharts.charts import Geo from pyecharts.faker import Faker from pyecharts.globals import GeoType, CurrentConfig CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/' c = ( Geo() .add_schema(maptype="广东", label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True)) .add( "热力图", [list(z) for z in zip(Faker.guangdong_city, Faker.values())], type_=GeoType.HEATMAP, ) .set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True)) .set_global_opts( visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(), title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Geo-广东地图") ) .render("geo_guangdong.html") )运行效果如下:
地图上批量添加经纬度数据
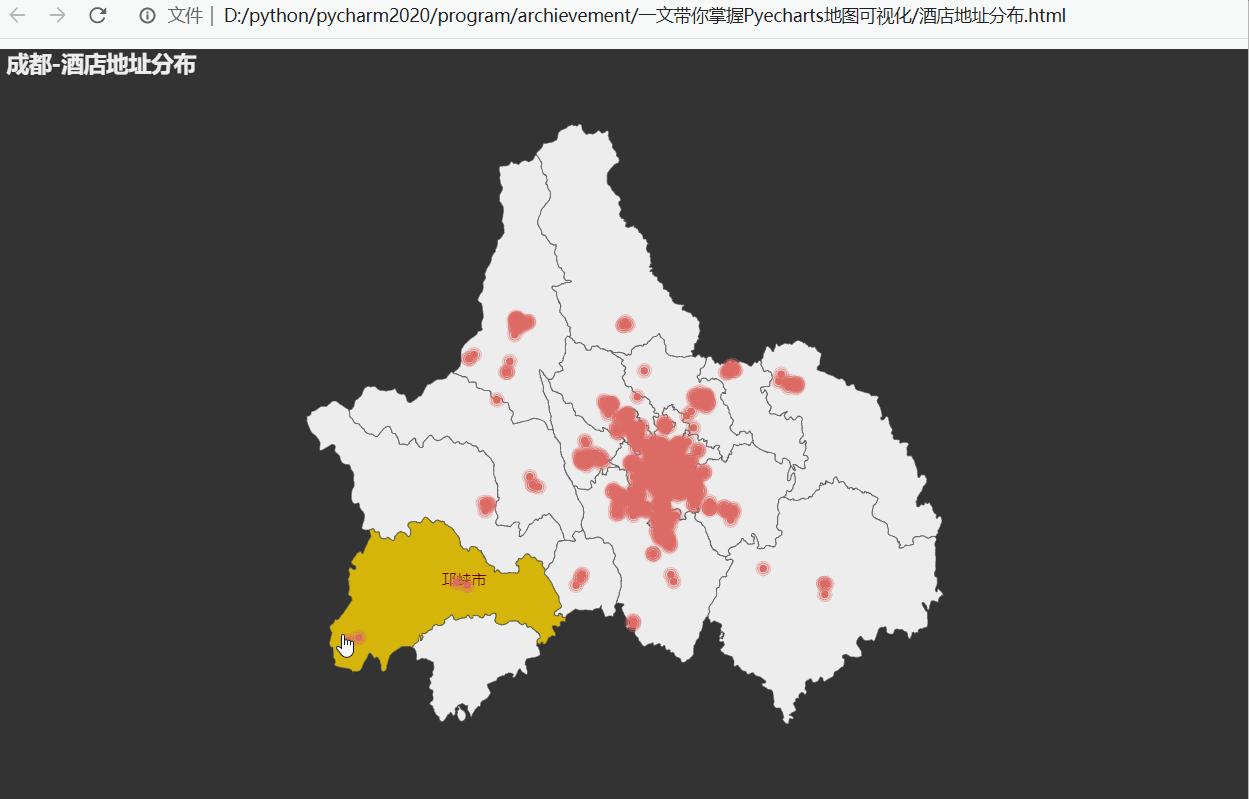
数据来源于美团网成都地区酒店信息,利用其中酒店的经纬度数据,批量添加在地图上可视化。
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- """ @File :demo5.py @Author :叶庭云 @CSDN :https://yetingyun.blog.csdn.net/ """ import pandas as pd from pyecharts.charts import Geo from pyecharts import options as opts from pyecharts.globals import GeoType, CurrentConfig, ThemeType CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/' # 读取Excel数据 数据来源美团网酒店信息 df = pd.read_excel("hotel.xlsx") # 获取 地点 经纬度信息 geo_sight_coord = {df.iloc[i]['酒店地址']: [df.iloc[i]['经度'], df.iloc[i]['纬度']] for i in range(len(df))} data = [(df['酒店地址'][j], f"{int(df['最低价'][j])}元(最低价)") for j in range(len(df))] # print(data) # print(geo_sight_coord) # 实例化Geo对象 导入成都地图 g = Geo(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.PURPLE_PASSION, width="1000px", height="600px")) g.add_schema(maptype="成都") for k, v in list(geo_sight_coord.items()): # 添加地址、经纬度数据 g.add_coordinate(k, v[0], v[1]) # 生成涟漪散点图 g.add("", data_pair=data, type_=GeoType.EFFECT_SCATTER, symbol_size=6) g.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False)) g.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="成都-酒店地址分布")) g.render("酒店地址分布.html")运行效果如下:
到此这篇关于一文带你掌握Pyecharts地理数据可视化的方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Pyecharts地理数据可视化内容请搜索python博客以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持python博客!
-
<< 上一篇 下一篇 >>
标签:pandas
一文带你掌握Pyecharts地理数据可视化的方法
看: 1532次 时间:2021-04-10 分类 : python教程
- 相关文章
- 2021-12-20Python 实现图片色彩转换案例
- 2021-12-20python初学定义函数
- 2021-12-20图文详解Python如何导入自己编写的py文件
- 2021-12-20python二分法查找实例代码
- 2021-12-20Pyinstaller打包工具的使用以及避坑
- 2021-12-20Facebook开源一站式服务python时序利器Kats详解
- 2021-12-20pyCaret效率倍增开源低代码的python机器学习工具
- 2021-12-20python机器学习使数据更鲜活的可视化工具Pandas_Alive
- 2021-12-20python读写文件with open的介绍
- 2021-12-20Python生成任意波形并存为txt的实现
-
搜索
-
-
推荐资源
-
Powered By python教程网 鲁ICP备18013710号
python博客 - 小白学python最友好的网站!