如下所示:
import requests url='http://www.baidu.com' #下面使用requests.request(method, url, **kwargs) re=requests.request('GET',url)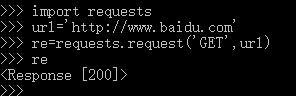
经验证,可用。
我们试着传入一个字典,首先用params参数。

结果为:
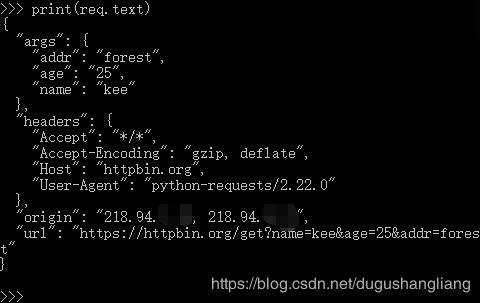
亮点在url和args。
我们还用get方法,把dic这个字典传给data试试看。
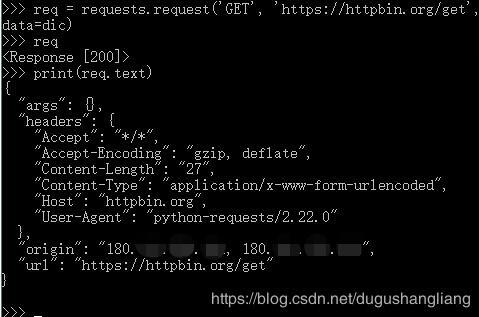
亮点还是在args和url。惊喜地发现,dic这个字典没传进去。
这是因为:

params是用来发送查询字符串,而data是用来发送正文的。post方法和get方法的特性是:这两种参数post方法都可以用,get方法只能发查询字符串,不能发送正文。
接下来试试看post方法:

上面这是用data参数传字典的,亮点在form。
再试试用params参数传这个字典:

亮点在url和args。
补充知识:python_request_三个参数
requests.request(method,url,**kwargs)
method:请求方法,对应get/put/post/delete/head/patch/options
url: 模拟获取页面的url连接
**kwrags:控制访问的参数,共13个
kwargs(13个参数):
(一)params
params:字典或者字节序列,作为参数增加到url中
例子:
import requests kv={“wd”:“你好”}#拼接的内容用字典储存 r=requests.request(“GET”,“http://www.baidu.com/s”,params=kv) print(r.url) print(r.text)运行后拼接的效果:http://www.baidu.com/s?wd=你好
(二)data
data:字典、字节、或文件对象,作为request
例子:
import requests kv={“key1”:“value1”,“key2”:“value2”} r=requests.request(“POST”,“http://httpbin.org/post”,data=kv) print(r.text)运行结果:
{ “args”: {}, “data”: “”, “files”: {}, “form”: { “key1”: “value1”, “key2”: “value2” }, “headers”: { “Accept”: “/”, “Accept-Encoding”: “gzip, deflate”, “Connection”: “close”, “Content-Length”: “23”, “Content-Type”: “application/x-www-form-urlencoded”, “Host”: “httpbin.org”, “User-Agent”: “python-requests/2.18.1” }, “json”: null, “origin”: “113.235.118.39”, “url”: “http://httpbin.org/post” }(三)json
json:JSON格式的数据,作为request的内容
(四)header
header:字典,http定制头
例子:
import requests hd={‘user-agent':“Chrome/10”}#改变浏览器模拟 r=requests.request(“post”,“http://www.baidu.com”,headers=hd(五)cookies:
cookies:字典或CookieJar,request中的cookie
(六)auth
auth:元组,支持HTTP认证功能
(七)files:
files:字典类型,传输文件
(八)tiemout
timeout:设定时间
(九)proxies
proxies:字典类型,设定访问代理服务器,可以增加登录认证
以上这篇python requests包的request()函数中的参数-params和data的区别介绍就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持python博客。
-
<< 上一篇 下一篇 >>
标签:requests
python requests包的request()函数中的参数-params和data的区别介绍
看: 1571次 时间:2020-07-12 分类 : python爬虫
- 相关文章
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫基础之爬虫的分类知识总结
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫基础讲解之请求
- 2021-07-20PyQt5爬取12306车票信息程序的实现
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫之m3u8文件里提取小视频的正确姿势
- 2021-07-20如何用python抓取B站数据
- 2021-07-20快速搭建python爬虫管理平台
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫之获取心知天气API实时天气数据并弹窗提醒
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫之批量下载喜马拉雅音频
- 2021-07-20python使用pywinauto驱动微信客户端实现公众号爬虫
- 2021-07-20Requests什么的通通爬不了的Python超强反爬虫方案!
-
搜索
-
-
推荐资源
-
Powered By python教程网 鲁ICP备18013710号
python博客 - 小白学python最友好的网站!