一 卷积操作:在pytorch搭建起网络时,大家通常都使用已有的框架进行训练,在网络中使用最多就是卷积操作,最熟悉不过的就是
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True)通过上面的输入发现想自定义自己的卷积核,比如高斯核,发现是行不通的,因为上面的参数里面只有卷积核尺寸,而权值weight是通过梯度一直更新的,是不确定的。
二 需要自己定义卷积核的目的:目前是需要通过一个VGG网络提取特征特后需要对其进行高斯卷积,卷积后再继续输入到网络中训练。
三 解决方案。使用
torch.nn.functional.conv2d(input, weight, bias=None, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1)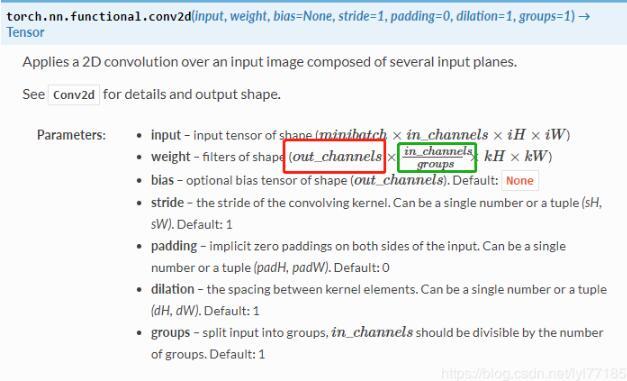
这里注意下weight的参数。与nn.Conv2d的参数不一样
可以发现F.conv2d可以直接输入卷积的权值weight,也就是卷积核。那么接下来就要首先生成一个高斯权重了。这里不直接一步步写了,直接输入就行。
kernel = [[0.03797616, 0.044863533, 0.03797616], [0.044863533, 0.053, 0.044863533], [0.03797616, 0.044863533, 0.03797616]]四 完整代码
class GaussianBlur(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(GaussianBlur, self).__init__() kernel = [[0.03797616, 0.044863533, 0.03797616], [0.044863533, 0.053, 0.044863533], [0.03797616, 0.044863533, 0.03797616]] kernel = torch.FloatTensor(kernel).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0) self.weight = nn.Parameter(data=kernel, requires_grad=False) def forward(self, x): x1 = x[:, 0] x2 = x[:, 1] x3 = x[:, 2] x1 = F.conv2d(x1.unsqueeze(1), self.weight, padding=2) x2 = F.conv2d(x2.unsqueeze(1), self.weight, padding=2) x3 = F.conv2d(x3.unsqueeze(1), self.weight, padding=2) x = torch.cat([x1, x2, x3], dim=1) return x这里为了网络模型需要写成了一个类,这里假设输入的x也就是经过网络提取后的三通道特征图(当然不一定是三通道可以是任意通道)
如果是任意通道的话,使用torch.expand()向输入的维度前面进行扩充。如下:
def blur(self, tensor_image): kernel = [[0.03797616, 0.044863533, 0.03797616], [0.044863533, 0.053, 0.044863533], [0.03797616, 0.044863533, 0.03797616]] min_batch=tensor_image.size()[0] channels=tensor_image.size()[1] out_channel=channels kernel = torch.FloatTensor(kernel).expand(out_channel,channels,3,3) self.weight = nn.Parameter(data=kernel, requires_grad=False) return F.conv2d(tensor_image,self.weight,1,1)以上这篇pytorch 自定义卷积核进行卷积操作方式就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持python博客。
-
<< 上一篇 下一篇 >>
pytorch 自定义卷积核进行卷积操作方式
看: 1426次 时间:2020-12-22 分类 : python教程
- 相关文章
- 2021-12-20Python 实现图片色彩转换案例
- 2021-12-20python初学定义函数
- 2021-12-20图文详解Python如何导入自己编写的py文件
- 2021-12-20python二分法查找实例代码
- 2021-12-20Pyinstaller打包工具的使用以及避坑
- 2021-12-20Facebook开源一站式服务python时序利器Kats详解
- 2021-12-20pyCaret效率倍增开源低代码的python机器学习工具
- 2021-12-20python机器学习使数据更鲜活的可视化工具Pandas_Alive
- 2021-12-20python读写文件with open的介绍
- 2021-12-20Python生成任意波形并存为txt的实现
-
搜索
-
-
推荐资源
-
Powered By python教程网 鲁ICP备18013710号
python博客 - 小白学python最友好的网站!