爬虫利器BeautifulSoup中find和find_all的使用方法
二话不说,先上段HTML例子
<html> <head> <title> index </title> </head> <body> <div> <ul> <li id="flask"class="item-0"><a href="link1.html" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >first item</a></li> <li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >second item</a></li> <li class="item-inactie"><a href="link3.html" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >third item</a></li> <li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >fourth item</a></li> <li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >fifth item</a> </ul> </div> <li> hello world </li> </body> </html>使用BeautifulSoup前需要先构建BeautifulSoup实例
# 构建beautifulsoup实例 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') # 第一个参数是要匹配的内容 # 第二个参数是beautifulsoup要采用的模块,即规则需要注意的是,导入对的模块需要事先安装,此处导入的LXML事先已经安装。可以导入的模块可通过查询BeautifulSoup的文档查看
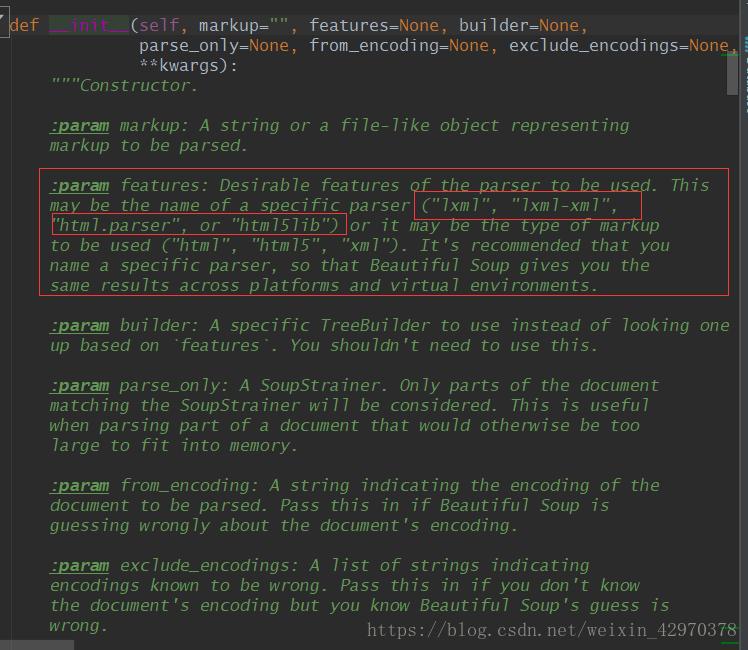
接下来是find和find_all的介绍
1. find
只返回第一个匹配到的对象
语法:
find(name, attrs, recursive, text, **wargs) # recursive 递归的,循环的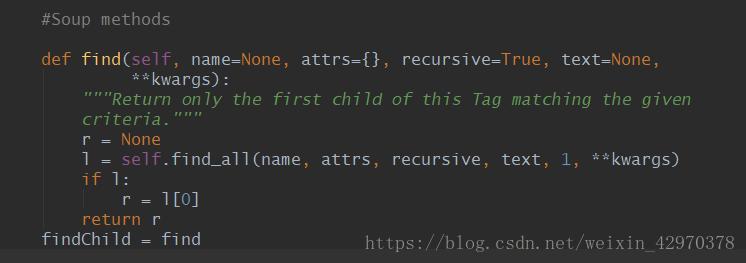
参数:
参数名 作用 name 查找标签 text 查找文本 attrs 基于attrs参数 例子:
# find查找一次 li = soup.find('li') print('find_li:',li) print('li.text(返回标签的内容):',li.text) print('li.attrs(返回标签的属性):',li.attrs) print('li.string(返回标签内容为字符串):',li.string)运行结果:
find_li:
- first item
li.text(返回标签的内容): first item
li.attrs(返回标签的属性): {'id': 'flask', 'class': ['item-0']}
li.string(返回标签内容为字符串): first itemfind也可以通过‘属性=值'的方法进行匹配
li = soup.find(id = 'flask') print(li,'\n')<li class="item-0" id="flask"><a href="link1.html" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >first item</a></li>需要注意的是,因为class是python的保留关键字,若要匹配标签内class的属性,需要特殊的方法,有以下两种:
- 在attrs属性用字典的方式进行参数传递
- BeautifulSoup自带的特别关键字class_
# 第一种:在attrs属性用字典进行传递参数 find_class = soup.find(attrs={'class':'item-1'}) print('findclass:',find_class,'\n') # 第二种:BeautifulSoup中的特别关键字参数class_ beautifulsoup_class_ = soup.find(class_ = 'item-1') print('BeautifulSoup_class_:',beautifulsoup_class_,'\n')运行结果
findclass:
- second item
BeautifulSoup_class_:
- second item
2. find_all
返回所有匹配到的结果,区别于find(find只返回查找到的第一个结果)
语法:
find_all(name, attrs, recursive, text, limit, **kwargs)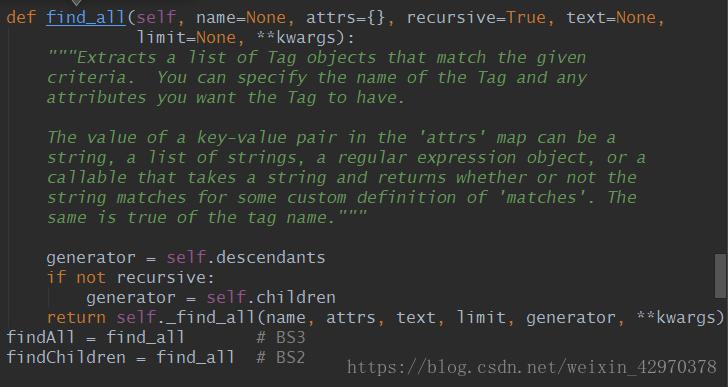
参数名 作用 name 查找标签 text 查找文本 attrs 基于attrs参数 与find一样的语法
上代码
# find_all 查找所有 li_all = soup.find_all('li') for li_all in li_all: print('---') print('匹配到的li:',li_all) print('li的内容:',li_all.text) print('li的属性:',li_all.attrs)运行结果:
---
匹配到的li:- first item
li的内容: first item
li的属性: {'id': 'flask', 'class': ['item-0']}
---
匹配到的li:- second item
li的内容: second item
li的属性: {'class': ['item-1']}
---
匹配到的li:- third item
li的内容: third item
li的属性: {'cvlass': 'item-inactie'}
---
匹配到的li:- fourth item
li的内容: fourth item
li的属性: {'class': ['item-1']}
---
匹配到的li:- fifth item
li的内容: fifth item附上比较灵活的find_all查询方法:
# 最灵活的使用方式 li_quick = soup.find_all(attrs={'class':'item-1'}) for li_quick in li_quick: print('最灵活的查找方法:',li_quick)运行结果:
- 最灵活的查找方法:
- second item
- 最灵活的查找方法:
- fourth item
完整代码:
# coding=utf8 # @Author= CaiJunxuan # @QQ=469590490 # @Wechat:15916454524 # beautifulsoup # 导入beautifulsoup模块 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # HTML例子 html = ''' <html> <head> <title> index </title> </head> <body> <div> <ul> <li id="flask"class="item-0"><a href="link1.html" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >first item</a></li> <li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >second item</a></li> <li cvlass="item-inactie"><a href="link3.html" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >third item</a></li> <li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >fourth item</a></li> <li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >fifth item</a> </ul> </div> <li> hello world </li> </body> </html> ''' # 构建beautifulsoup实例 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') # 第一个参数是要匹配的内容 # 第二个参数是beautifulsoup要采用的模块,即规则 # html.parser是python内置的结构匹配方法,但是效率不如lxml所以不常用 # lxml 采用lxml模块 # html5lib,该模块可以将内容转换成html5对象 # 若想要以上功能,就需要具备对应的模块,比如使用lxml就要安装lxml # 在bs4当中有很多种匹配方法,但常用有两种: # find查找一次 li = soup.find('li') print('find_li:',li) print('li.text(返回标签的内容):',li.text) print('li.attrs(返回标签的属性):',li.attrs) print('li.string(返回标签内容为字符串):',li.string) print(50*'*','\n') # find可以通过'属性 = 值'的方法进行select li = soup.find(id = 'flask') print(li,'\n') # 因为class是python的保留关键字,所以无法直接查找class这个关键字 # 有两种方法可以进行class属性查询 # 第一种:在attrs属性用字典进行传递参数 find_class = soup.find(attrs={'class':'item-1'}) print('findclass:',find_class,'\n') # 第二种:BeautifulSoup中的特别关键字参数class_ beautifulsoup_class_ = soup.find(class_ = 'item-1') print('BeautifulSoup_class_:',beautifulsoup_class_,'\n') # find_all 查找所有 li_all = soup.find_all('li') for li_all in li_all: print('---') print('匹配到的li:',li_all) print('li的内容:',li_all.text) print('li的属性:',li_all.attrs) # 最灵活的使用方式 li_quick = soup.find_all(attrs={'class':'item-1'}) for li_quick in li_quick: print('最灵活的查找方法:',li_quick)到此这篇关于BeautifulSoup中find和find_all的使用详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关BeautifulSoup find和find_all内容请搜索python博客以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持python博客!
- << 上一篇 下一篇 >>
BeautifulSoup中find和find_all的使用详解
看: 1577次 时间:2020-12-11 分类 : python爬虫
- 相关文章
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫基础之爬虫的分类知识总结
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫基础讲解之请求
- 2021-07-20PyQt5爬取12306车票信息程序的实现
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫之m3u8文件里提取小视频的正确姿势
- 2021-07-20如何用python抓取B站数据
- 2021-07-20快速搭建python爬虫管理平台
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫之获取心知天气API实时天气数据并弹窗提醒
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫之批量下载喜马拉雅音频
- 2021-07-20python使用pywinauto驱动微信客户端实现公众号爬虫
- 2021-07-20Requests什么的通通爬不了的Python超强反爬虫方案!
-
搜索
-
-
推荐资源
-
Powered By python教程网 鲁ICP备18013710号
python博客 - 小白学python最友好的网站!