1、PIL介绍以及图片分割
Python 3 安装: pip3 install Pillow
1.1 image 模块
Image模块是在Python PIL图像处理中常见的模块,主要是用于对这个图像的基本处理,它配合open、save、convert、show…等功能使用。
from PIL import Image #打开文件代表打开pycharm中的文件 im = Image.open('1.jpg') #展示图片 im.show()1、Crop类
拷贝这个图像。如果用户想粘贴一些数据到这张图,可以使用这个方法,但是原始图像不会受到影响。
im.crop(box) ⇒ image从当前的图像中返回一个矩形区域的拷贝。变量box是一个四元组,定义了左、上、右和下的像素坐标。用来表示在原始图像中截取的位置坐标,如box(100,100,200,200)就表示在原始图像中以左上角为坐标原点,截取一个100*100(像素为单位)的图像。
from PIL import Image im = Image.open("pic1.jpg") ##确定拷贝区域大小 box = (5, 41, 72, 108) ##将im表示的图片对象拷贝到region中,大小为box region = im.crop(box) region.show()
实战一:12306图像分割并保存
from PIL import Image #切割图像,由于下载的图片都是有固定的位置,所以直接控制像素进行切割就行了 def cut_img(im, x, y): assert 0 <= x <= 3 assert 0 <= y <= 2 left = 5 + (67 + 5) * x top = 41 + (67 + 5) * y right = left + 67 bottom = top + 67 return im.crop((left, top, right, bottom)) if __name__ == '__main__': im = Image.open("./pic1.jpg") #控制y轴 for y in range(2): #控制x轴 for x in range(4): im2 = cut_img(im, x, y) im2.save('./images/%s_%s.png'%(y,x))
2、百度平台接口实现
2.1.平台接入:
1.打开https://ai.baidu.com/进入控制台,选择文字识别服务。

2.创建应用,如图示:
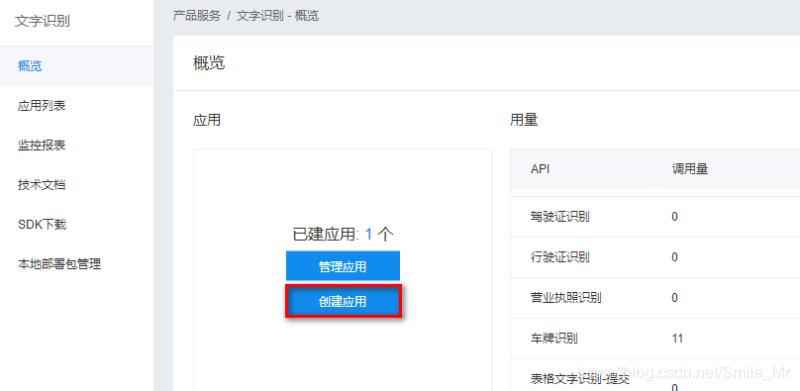
3.输入应用名称、描述,并选择应用类型,之后点击“立即创建”按钮。
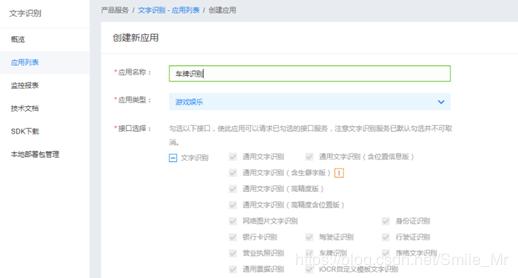
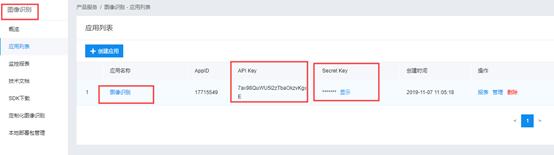
4.创建完毕,点击“返回应用列表”。

5.此处显示AK,SK,后面程序中会用到
3. 官方文档的读取
1.打开https://ai.baidu.com/docs#/OCR-API/top 文档说明
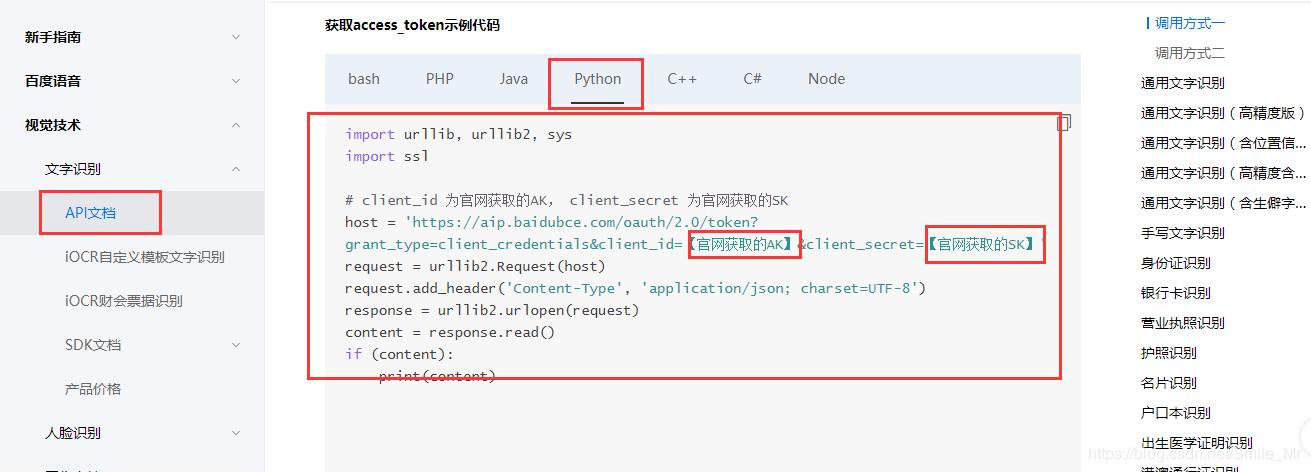
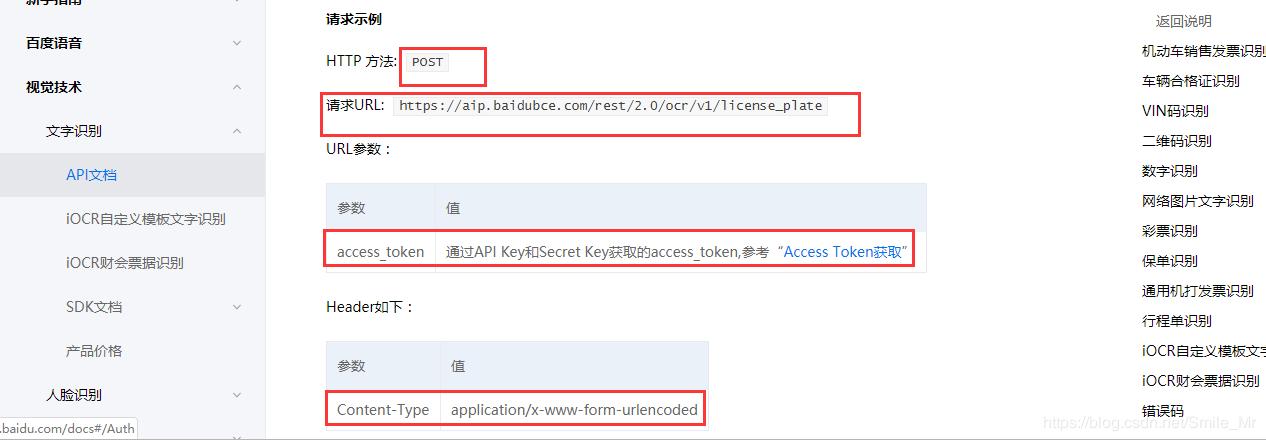
需要用到的信息有:
(1)图像识别URL: https://aip.baidubce.com/rest/2.0/image-classify/v2/advanced_general
(2)Header格式:Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded
(3) 请求参数:image和multi_detect两个参数,image为图像数据,base64编码后进行urlencode,要求base64编码和urlencode后大小不超过4M。
(4)返回参数:车牌颜色Color、车牌号码number等。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import base64 import requests import os import time #todo:获取百度权限验证码access_token def get_token(): get_token_url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/oauth/2.0/token" params = { "grant_type": "client_credentials", "client_id": "7ax98QuWU5l2zTbaOkzvKgxE", "client_secret": "INugQTM2DAfNFgfxtvgR7eF8AHPFGP5t", } res = requests.get(get_token_url, params).json() return res["access_token"] #todo:通过权限验证码和图片进行识别物品 def get_result(access_token,image): url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/rest/2.0/image-classify/v2/advanced_general" #打开文件并进行编码 with open(image, 'rb')as f: image = base64.b64encode(f.read()) # image = #头部信息 headers = { 'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' } #发送数据 data = { "access_token": access_token, "image": image } #发送请求,并返回识别数据 res = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=data).json() if res: result = res['result'] return result #todo:获取图片关键物品 def get_keywords(result): #按照最大匹配率进行排序,并获取左最后一个 max_score = sorted(result,key=lambda x:x['score'])[-1] # print(max_score['keyword']) keyword = max_score['keyword'] return keyword if __name__ == '__main__': access_token = get_token() get_result(access_token,'pic1.jpg') datas = [] for root,dir,files in os.walk('images'): for file in files: image = os.path.join(root,file) result = get_result(access_token,image) keyword = get_keywords(result) print(keyword) time.sleep(1) datas.append(keyword) print(datas)
总结:
- PIL介绍以及图片分割
- 百度AI图像识别实例搭建
- 识别12306类别码
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持python博客。
-
<< 上一篇 下一篇 >>
标签:requests
Python 识别12306图片验证码物品的实现示例
看: 1491次 时间:2020-10-30 分类 : python教程
- 相关文章
- 2021-12-20Python 实现图片色彩转换案例
- 2021-12-20python初学定义函数
- 2021-12-20图文详解Python如何导入自己编写的py文件
- 2021-12-20python二分法查找实例代码
- 2021-12-20Pyinstaller打包工具的使用以及避坑
- 2021-12-20Facebook开源一站式服务python时序利器Kats详解
- 2021-12-20pyCaret效率倍增开源低代码的python机器学习工具
- 2021-12-20python机器学习使数据更鲜活的可视化工具Pandas_Alive
- 2021-12-20python读写文件with open的介绍
- 2021-12-20Python生成任意波形并存为txt的实现
-
搜索
-
-
推荐资源
-
Powered By python教程网 鲁ICP备18013710号
python博客 - 小白学python最友好的网站!