背景知识:
FigureCanvasXAgg就是一个渲染器,渲染器的工作就是drawing,执行绘图的这个动作。渲染器是使物体显示在屏幕上
主要内容:
将一个figure渲染的canvas变为一个Qt widgets,figure显示的过程是需要管理器(manager),需要FigureCanvasBase来管理。报错信息'FigureCanvasQTAgg' object has no attribute 'manager'
将一个navigation toolbar渲染成Qt widgets
使用用户事件来实时更新matplotlib plot
matplotlib针对GUI设计了两层结构概念:canvas,renderer。
下面我将以默认自带的后端 tkAgg:from matplotlib.backends.backend_tkagg import FigureCanvasTkAgg as FigureCanvas为例,为大家讲解画布与渲染器的知识。
一. canvas(画布)
对应抽象的类:FigureCanvasBase and FigureManagerBase
作用:
保存对图像的引用
更新图像通过对画布的引用
定义运行注册的事件方法
将本地工具箱事件转为matplotlib事件抽象框架
定义绘制渲染图片的方法
停止和开始nono-GUI事件循环
1. 追寻matplotlib.figure.Figure.show( )
以下引自matplotlib.figure.Figure.show( ) 源码和注释:
#matplotlib.figure.Figure.show( ) def show(self, warn=True): """ If using a GUI backend with pyplot, display the figure window. If the figure was not created using :func:`~matplotlib.pyplot.figure`, it will lack a :class:`~matplotlib.backend_bases.FigureManagerBase`, and will raise an AttributeError. Parameters ---------- warm : bool If ``True``, issue warning when called on a non-GUI backend Notes ----- For non-GUI backends, this does nothing, in which case a warning will be issued if *warn* is ``True`` (default). """ try: manager = getattr(self.canvas, 'manager') except AttributeError as err: raise AttributeError("%s\n" "Figure.show works only " "for figures managed by pyplot, normally " "created by pyplot.figure()." % err) if manager is not None: try: manager.show() return except NonGuiException: pass它是通过manager.show()来实现画图的动作的。
2. 追寻plt.show()
而在==plt.show( )==的源码中我们可以查到:
#plt.show() from matplotlib.backends import pylab_setup _show = pylab_setup() def show(*args, **kw): global _show return _show(*args, **kw)而我们继续查找就得到了,这是在backends包的__init__.py模块里的代码,代码说了一大堆,无非就是说它返回了四个对象:backend_mod, new_figure_manager, draw_if_interactive, show。而show就是show = getattr(backend_mod, 'show', do_nothing_show)得到的其中backend_mod就是要导入模块的绝对路径,之后验证的show就是matplotlib.backends.backend_tkagg._BackendTkAgg,继续追寻之后我们得到class _BackendTkAgg(_BackendTk): FigureCanvas = FigureCanvasTkAgg,之后我们用help函数得到
show(block=None) method of builtins.type instance Show all figures. `show` blocks by calling `mainloop` if *block* is ``True``, or if it is ``None`` and we are neither in IPython's ``%pylab`` mode, nor in `interactive` mode.我们继续刨根,寻找从FigureCanvas开始的类的关系和其方法,类的继承结构关系如下图
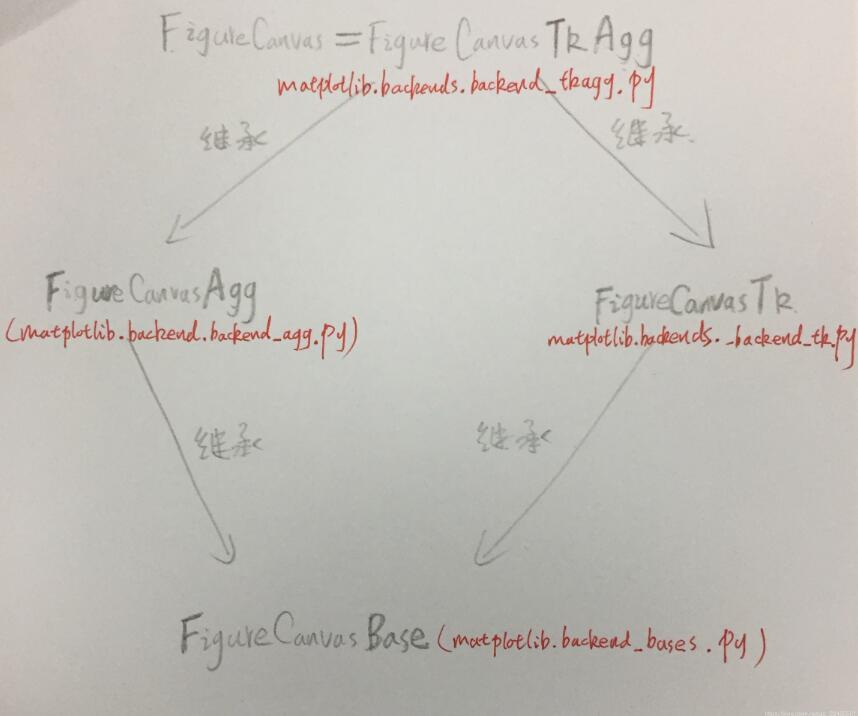
然后终于在FigureCnavasTk类的声明中找到了这样的一句声明:
show = cbook.deprecated("2.2", name="FigureCanvasTk.show", alternative="FigureCanvasTk.draw")( lambda self: self.draw())也就是说show归根结底是backend里的一个FigureCanvasTk.draw()的一个变形 !
pylab_setup代码如下:
def pylab_setup(name=None): '''return new_figure_manager, draw_if_interactive and show for pyplot This provides the backend-specific functions that are used by pyplot to abstract away the difference between interactive backends. Parameters ---------- name : str, optional The name of the backend to use. If `None`, falls back to ``matplotlib.get_backend()`` (which return :rc:`backend`). ''' # Import the requested backend into a generic module object if name is None: # validates, to match all_backends name = matplotlib.get_backend() if name.startswith('module://'): backend_name = name[9:] else: backend_name = 'backend_' + name backend_name = backend_name.lower() # until we banish mixed case backend_name = 'matplotlib.backends.%s' % backend_name.lower() # the last argument is specifies whether to use absolute or relative # imports. 0 means only perform absolute imports. #得到模块的绝对路径backend_mod,然后通过绝对路径加.就可以调用各个抽象类 #<module 'matplotlib.backends.backend_tkagg' from 'D:\\Python36\\lib\\site-packages\\matplotlib\\backends\\backend_tkagg.py'>默认实验的! backend_mod = __import__(backend_name, globals(), locals(), [backend_name], 0) # Things we pull in from all backends new_figure_manager = backend_mod.new_figure_manager # image backends like pdf, agg or svg do not need to do anything # for "show" or "draw_if_interactive", so if they are not defined # by the backend, just do nothing def do_nothing_show(*args, **kwargs): frame = inspect.currentframe() fname = frame.f_back.f_code.co_filename if fname in ('<stdin>', '<ipython console>'): warnings.warn(""" Your currently selected backend, '%s' does not support show(). Please select a GUI backend in your matplotlibrc file ('%s') or with matplotlib.use()""" % (name, matplotlib.matplotlib_fname())) def do_nothing(*args, **kwargs): pass backend_version = getattr(backend_mod, 'backend_version', 'unknown') show = getattr(backend_mod, 'show', do_nothing_show) draw_if_interactive = getattr(backend_mod, 'draw_if_interactive', do_nothing) _log.debug('backend %s version %s', name, backend_version) # need to keep a global reference to the backend for compatibility # reasons. See https://github.com/matplotlib/matplotlib/issues/6092 global backend backend = name return backend_mod, new_figure_manager, draw_if_interactive, show3. 追寻plt.figure()
我们创建的这个figure必须有manager,否则则会报错,如果是plt.figure初始化的,plt.figure( )源码如下:
plt.figure()示例
def figure(): figManager = _pylab_helpers.Gcf.get_fig_manager(num) figManager = new_figure_manager(num,figsize=figsize,dpi=dpi,facecolor=facecolor,edgecolor=edgecolor,frameon=frameon,FigureClass=FigureClass,**kwargs) ...... ...... return figManager.canvas.figure4. 追寻matplotlib.figure.Figure()
而在matplotlib.figure.Figure() 中,其初始化函数__init__(),并没有默认生成manager这个属性,所以在调用show的时候,就会报错!如上其show函数定义的那样
def __init__(self, figsize=None, # defaults to rc figure.figsize dpi=None, # defaults to rc figure.dpi facecolor=None, # defaults to rc figure.facecolor edgecolor=None, # defaults to rc figure.edgecolor linewidth=0.0, # the default linewidth of the frame frameon=None, # whether or not to draw the figure frame subplotpars=None, # default to rc tight_layout=None, # default to rc figure.autolayout constrained_layout=None, # default to rc #figure.constrained_layout.use ): """ Parameters ---------- figsize : 2-tuple of floats ``(width, height)`` tuple in inches dpi : float Dots per inch facecolor The figure patch facecolor; defaults to rc ``figure.facecolor`` edgecolor The figure patch edge color; defaults to rc ``figure.edgecolor`` linewidth : float The figure patch edge linewidth; the default linewidth of the frame frameon : bool If ``False``, suppress drawing the figure frame subplotpars : :class:`SubplotParams` Subplot parameters, defaults to rc tight_layout : bool If ``False`` use *subplotpars*; if ``True`` adjust subplot parameters using `.tight_layout` with default padding. When providing a dict containing the keys ``pad``, ``w_pad``, ``h_pad``, and ``rect``, the default `.tight_layout` paddings will be overridden. Defaults to rc ``figure.autolayout``. constrained_layout : bool If ``True`` use constrained layout to adjust positioning of plot elements. Like ``tight_layout``, but designed to be more flexible. See :doc:`/tutorials/intermediate/constrainedlayout_guide` for examples. (Note: does not work with :meth:`.subplot` or :meth:`.subplot2grid`.) Defaults to rc ``figure.constrained_layout.use``. """ Artist.__init__(self) # remove the non-figure artist _axes property # as it makes no sense for a figure to be _in_ an axes # this is used by the property methods in the artist base class # which are over-ridden in this class del self._axes self.callbacks = cbook.CallbackRegistry() if figsize is None: figsize = rcParams['figure.figsize'] if dpi is None: dpi = rcParams['figure.dpi'] if facecolor is None: facecolor = rcParams['figure.facecolor'] if edgecolor is None: edgecolor = rcParams['figure.edgecolor'] if frameon is None: frameon = rcParams['figure.frameon'] if not np.isfinite(figsize).all(): raise ValueError('figure size must be finite not ' '{}'.format(figsize)) self.bbox_inches = Bbox.from_bounds(0, 0, *figsize) self.dpi_scale_trans = Affine2D().scale(dpi, dpi) # do not use property as it will trigger self._dpi = dpi self.bbox = TransformedBbox(self.bbox_inches, self.dpi_scale_trans) self.frameon = frameon self.transFigure = BboxTransformTo(self.bbox) self.patch = Rectangle( xy=(0, 0), width=1, height=1, facecolor=facecolor, edgecolor=edgecolor, linewidth=linewidth) self._set_artist_props(self.patch) self.patch.set_aa(False) self._hold = rcParams['axes.hold'] if self._hold is None: self._hold = True self.canvas = None self._suptitle = None if subplotpars is None: subplotpars = SubplotParams() self.subplotpars = subplotpars # constrained_layout: self._layoutbox = None # set in set_constrained_layout_pads() self.set_constrained_layout(constrained_layout) self.set_tight_layout(tight_layout) self._axstack = AxesStack() # track all figure axes and current axes self.clf() self._cachedRenderer = None # groupers to keep track of x and y labels we want to align. # see self.align_xlabels and self.align_ylabels and # axis._get_tick_boxes_siblings self._align_xlabel_grp = cbook.Grouper() self._align_ylabel_grp = cbook.Grouper()综上所述,我们通过matplotlib.figure.Figure()来创建得到的fig,并不具备manager的属性,而通过plt.figure()创建的fig,就默认创建了manager。
二 . renderer(渲染器),默认是tkagg
对应抽象的类:RendererBase and GraphicsContextBase
作用:
- 很多渲染操作都传递给一个额外的抽象:GraphicsContextBase,它为处理颜色、线条样式、起始样式、混合属性和反混叠选项等的代码提供了一个干净的分离。
Qt & matplotlib示例代码
#import modules from Matplotlib from matplotlib.backends.backend_qt4agg import FigureCanvasQTAgg as FigureCanvas from matplotlib.backends.backend_qt4agg import NavigationToolbar2QTAgg as NavigationToolbar import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #import random module to generate set import random class Window(QtGui.QDialog): def __init__(self, parent=None): super(Window, self).__init__(parent) #init figure and canvas self.figure = plt.figure() self.canvas = FigureCanvas(self.figure) #init nav toolbar self.toolbar = NavigationToolbar(self.canvas, self) # Add plot button self.button = QtGui.QPushButton('Plot') # connect button to custom slot (see later) self.button.clicked.connect(self.plot) # set the layout layout = QtGui.QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.toolbar) layout.addWidget(self.canvas) layout.addWidget(self.button) self.setLayout(layout) ### our custom slot def plot(self): # random data data = [random.random() for i in range(25)] # create an axis ax = self.figure.add_subplot(1,1,1) # discards the old graph ax.hold(False) # plot data ax.plot(data, '*') # refresh canvas self.canvas.draw()三. Problems(GUI画3D不能旋转)
一个Axes3D创建callback函数给画布上的图形实现旋转特性。如果说先给图形(figure)增加axes或者其他配件的时候,在之后将图形附加到画布的时候,之前添加的axes的callback函数可能不能够接收消息事件,也就没办法在绘出的GUI实现旋转的性能。
所以应该先将图形附加到画布上,然后再对图形增加axes和其他的配件。
FigureCanvas(figure,canvas)
figure:需要附加的图形(添加者),canvas提供渲染功能的对象(承载者)
每一次你调用FigureCanvas()的时候,你都是将图形附加到新画布上(这不是你所看到的的那个canvas),于是 the call-backs函数将不会被射击(接收事件信号),因为他们正在监听一个你看不到的canvas。
四 . 附录
以上这篇浅谈matplotlib中FigureCanvasXAgg的用法就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持python博客。
-
<< 上一篇 下一篇 >>
标签:matplotlib
浅谈matplotlib中FigureCanvasXAgg的用法
看: 1538次 时间:2020-09-18 分类 : python教程
- 相关文章
- 2021-12-20Python 实现图片色彩转换案例
- 2021-12-20python初学定义函数
- 2021-12-20图文详解Python如何导入自己编写的py文件
- 2021-12-20python二分法查找实例代码
- 2021-12-20Pyinstaller打包工具的使用以及避坑
- 2021-12-20Facebook开源一站式服务python时序利器Kats详解
- 2021-12-20pyCaret效率倍增开源低代码的python机器学习工具
- 2021-12-20python机器学习使数据更鲜活的可视化工具Pandas_Alive
- 2021-12-20python读写文件with open的介绍
- 2021-12-20Python生成任意波形并存为txt的实现
-
搜索
-
-
推荐资源
-
Powered By python教程网 鲁ICP备18013710号
python博客 - 小白学python最友好的网站!