一、K.prod
prod
keras.backend.prod(x, axis=None, keepdims=False)
功能:在某一指定轴,计算张量中的值的乘积。
参数
x: 张量或变量。
axis: 一个整数需要计算乘积的轴。
keepdims: 布尔值,是否保留原尺寸。 如果 keepdims 为 False,则张量的秩减 1。 如果 keepdims 为 True,缩小的维度保留为长度 1。
返回
x 的元素的乘积的张量。
Numpy 实现
def prod(x, axis=None, keepdims=False): if isinstance(axis, list): axis = tuple(axis) return np.prod(x, axis=axis, keepdims=keepdims)具体例子:
import numpy as np x=np.array([[2,4,6],[2,4,6]]) scaling = np.prod(x, axis=1, keepdims=False) print(x) print(scaling)【运行结果】
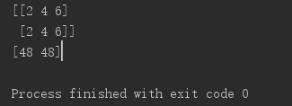
二、K.cast
cast
keras.backend.cast(x, dtype)
功能:将张量转换到不同的 dtype 并返回。
你可以转换一个 Keras 变量,但它仍然返回一个 Keras 张量。
参数
x: Keras 张量(或变量)。
dtype: 字符串, ('float16', 'float32' 或 'float64')。
返回
Keras 张量,类型为 dtype。
例子
>>> from keras import backend as K >>> input = K.placeholder((2, 3), dtype='float32') >>> input <tf.Tensor 'Placeholder_2:0' shape=(2, 3) dtype=float32> # It doesn't work in-place as below. >>> K.cast(input, dtype='float16') <tf.Tensor 'Cast_1:0' shape=(2, 3) dtype=float16> >>> input <tf.Tensor 'Placeholder_2:0' shape=(2, 3) dtype=float32> # you need to assign it. >>> input = K.cast(input, dtype='float16') >>> input <tf.Tensor 'Cast_2:0' shape=(2, 3) dtype=float16>补充知识:keras源码之backend库目录
backend库目录
先看common.py
一上来是一些说明
# the type of float to use throughout the session. 整个模块都是用浮点型数据 _FLOATX = 'float32' # 数据类型为32位浮点型 _EPSILON = 1e-7 # 很小的常数 _IMAGE_DATA_FORMAT = 'channels_last' # 图像数据格式 最后显示通道,tensorflow格式接下来看里面的一些函数
def epsilon(): """Returns the value of the fuzz factor used in numeric expressions. 返回数值表达式中使用的模糊因子的值 # Returns A float. # Example ```python >>> keras.backend.epsilon() 1e-07 ``` """ return _EPSILON该函数定义了一个常量,值为1e-07,在终端可以直接输出,如下:

def set_epsilon(e): """Sets the value of the fuzz factor used in numeric expressions. # Arguments e: float. New value of epsilon. # Example ```python >>> from keras import backend as K >>> K.epsilon() 1e-07 >>> K.set_epsilon(1e-05) >>> K.epsilon() 1e-05 ``` """ global _EPSILON _EPSILON = e该函数允许自定义值

以string的形式返回默认的浮点类型:
def floatx(): """Returns the default float type, as a string. (e.g. 'float16', 'float32', 'float64'). # Returns String, the current default float type. # Example ```python >>> keras.backend.floatx() 'float32' ``` """ return _FLOATX
把numpy数组投影到默认的浮点类型:
def cast_to_floatx(x): """Cast a Numpy array to the default Keras float type.把numpy数组投影到默认的浮点类型 # Arguments x: Numpy array. # Returns The same Numpy array, cast to its new type. # Example ```python >>> from keras import backend as K >>> K.floatx() 'float32' >>> arr = numpy.array([1.0, 2.0], dtype='float64') >>> arr.dtype dtype('float64') >>> new_arr = K.cast_to_floatx(arr) >>> new_arr array([ 1., 2.], dtype=float32) >>> new_arr.dtype dtype('float32') ``` """ return np.asarray(x, dtype=_FLOATX)默认数据格式、自定义数据格式和检查数据格式:
def image_data_format(): """Returns the default image data format convention ('channels_first' or 'channels_last'). # Returns A string, either `'channels_first'` or `'channels_last'` # Example ```python >>> keras.backend.image_data_format() 'channels_first' ``` """ return _IMAGE_DATA_FORMAT def set_image_data_format(data_format): """Sets the value of the data format convention. # Arguments data_format: string. `'channels_first'` or `'channels_last'`. # Example ```python >>> from keras import backend as K >>> K.image_data_format() 'channels_first' >>> K.set_image_data_format('channels_last') >>> K.image_data_format() 'channels_last' ``` """ global _IMAGE_DATA_FORMAT if data_format not in {'channels_last', 'channels_first'}: raise ValueError('Unknown data_format:', data_format) _IMAGE_DATA_FORMAT = str(data_format) def normalize_data_format(value): """Checks that the value correspond to a valid data format. # Arguments value: String or None. `'channels_first'` or `'channels_last'`. # Returns A string, either `'channels_first'` or `'channels_last'` # Example ```python >>> from keras import backend as K >>> K.normalize_data_format(None) 'channels_first' >>> K.normalize_data_format('channels_last') 'channels_last' ``` # Raises ValueError: if `value` or the global `data_format` invalid. """ if value is None: value = image_data_format() data_format = value.lower() if data_format not in {'channels_first', 'channels_last'}: raise ValueError('The `data_format` argument must be one of ' '"channels_first", "channels_last". Received: ' + str(value)) return data_format剩余的关于维度顺序和数据格式的方法:
def set_image_dim_ordering(dim_ordering): """Legacy setter for `image_data_format`. # Arguments dim_ordering: string. `tf` or `th`. # Example ```python >>> from keras import backend as K >>> K.image_data_format() 'channels_first' >>> K.set_image_data_format('channels_last') >>> K.image_data_format() 'channels_last' ``` # Raises ValueError: if `dim_ordering` is invalid. """ global _IMAGE_DATA_FORMAT if dim_ordering not in {'tf', 'th'}: raise ValueError('Unknown dim_ordering:', dim_ordering) if dim_ordering == 'th': data_format = 'channels_first' else: data_format = 'channels_last' _IMAGE_DATA_FORMAT = data_format def image_dim_ordering(): """Legacy getter for `image_data_format`. # Returns string, one of `'th'`, `'tf'` """ if _IMAGE_DATA_FORMAT == 'channels_first': return 'th' else: return 'tf'在common.py之后有三个backend,分别是cntk,tensorflow和theano。
__init__.py
首先从common.py中引入了所有需要的东西
from .common import epsilon from .common import floatx from .common import set_epsilon from .common import set_floatx from .common import cast_to_floatx from .common import image_data_format from .common import set_image_data_format from .common import normalize_data_format接下来是检查环境变量与配置文件,设置backend和format,默认的backend是tensorflow。
# Set Keras base dir path given KERAS_HOME env variable, if applicable. # Otherwise either ~/.keras or /tmp. if 'KERAS_HOME' in os.environ: # 环境变量 _keras_dir = os.environ.get('KERAS_HOME') else: _keras_base_dir = os.path.expanduser('~') if not os.access(_keras_base_dir, os.W_OK): _keras_base_dir = '/tmp' _keras_dir = os.path.join(_keras_base_dir, '.keras') # Default backend: TensorFlow. 默认后台是TensorFlow _BACKEND = 'tensorflow' # Attempt to read Keras config file.读取keras配置文件 _config_path = os.path.expanduser(os.path.join(_keras_dir, 'keras.json')) if os.path.exists(_config_path): try: with open(_config_path) as f: _config = json.load(f) except ValueError: _config = {} _floatx = _config.get('floatx', floatx()) assert _floatx in {'float16', 'float32', 'float64'} _epsilon = _config.get('epsilon', epsilon()) assert isinstance(_epsilon, float) _backend = _config.get('backend', _BACKEND) _image_data_format = _config.get('image_data_format', image_data_format()) assert _image_data_format in {'channels_last', 'channels_first'} set_floatx(_floatx) set_epsilon(_epsilon) set_image_data_format(_image_data_format) _BACKEND = _backend之后的tensorflow_backend.py文件是一些tensorflow中的函数说明,详细内容请参考tensorflow有关资料。
以上这篇浅谈keras中的后端backend及其相关函数(K.prod,K.cast)就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持python博客。
-
<< 上一篇 下一篇 >>
标签:numpy
浅谈keras中的后端backend及其相关函数(K.prod,K.cast)
看: 1630次 时间:2020-09-05 分类 : python教程
- 相关文章
- 2021-12-20Python 实现图片色彩转换案例
- 2021-12-20python初学定义函数
- 2021-12-20图文详解Python如何导入自己编写的py文件
- 2021-12-20python二分法查找实例代码
- 2021-12-20Pyinstaller打包工具的使用以及避坑
- 2021-12-20Facebook开源一站式服务python时序利器Kats详解
- 2021-12-20pyCaret效率倍增开源低代码的python机器学习工具
- 2021-12-20python机器学习使数据更鲜活的可视化工具Pandas_Alive
- 2021-12-20python读写文件with open的介绍
- 2021-12-20Python生成任意波形并存为txt的实现
-
搜索
-
-
推荐资源
-
Powered By python教程网 鲁ICP备18013710号
python博客 - 小白学python最友好的网站!