本文实例为爬取拉勾网上的python相关的职位信息, 这些信息在职位详情页上, 如职位名, 薪资, 公司名等等.
分析思路
分析查询结果页
在拉勾网搜索框中搜索'python'关键字, 在浏览器地址栏可以看到搜索结果页的url为: 'https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python?labelWords=&fromSearch=true&suginput=', 尝试将?后的参数删除, 发现访问结果相同.
打开Chrome网页调试工具(F12), 分析每条搜索结果(即每个职位)在html中所处的元素定位, 发现每条结果都在
- 下的li标签中.
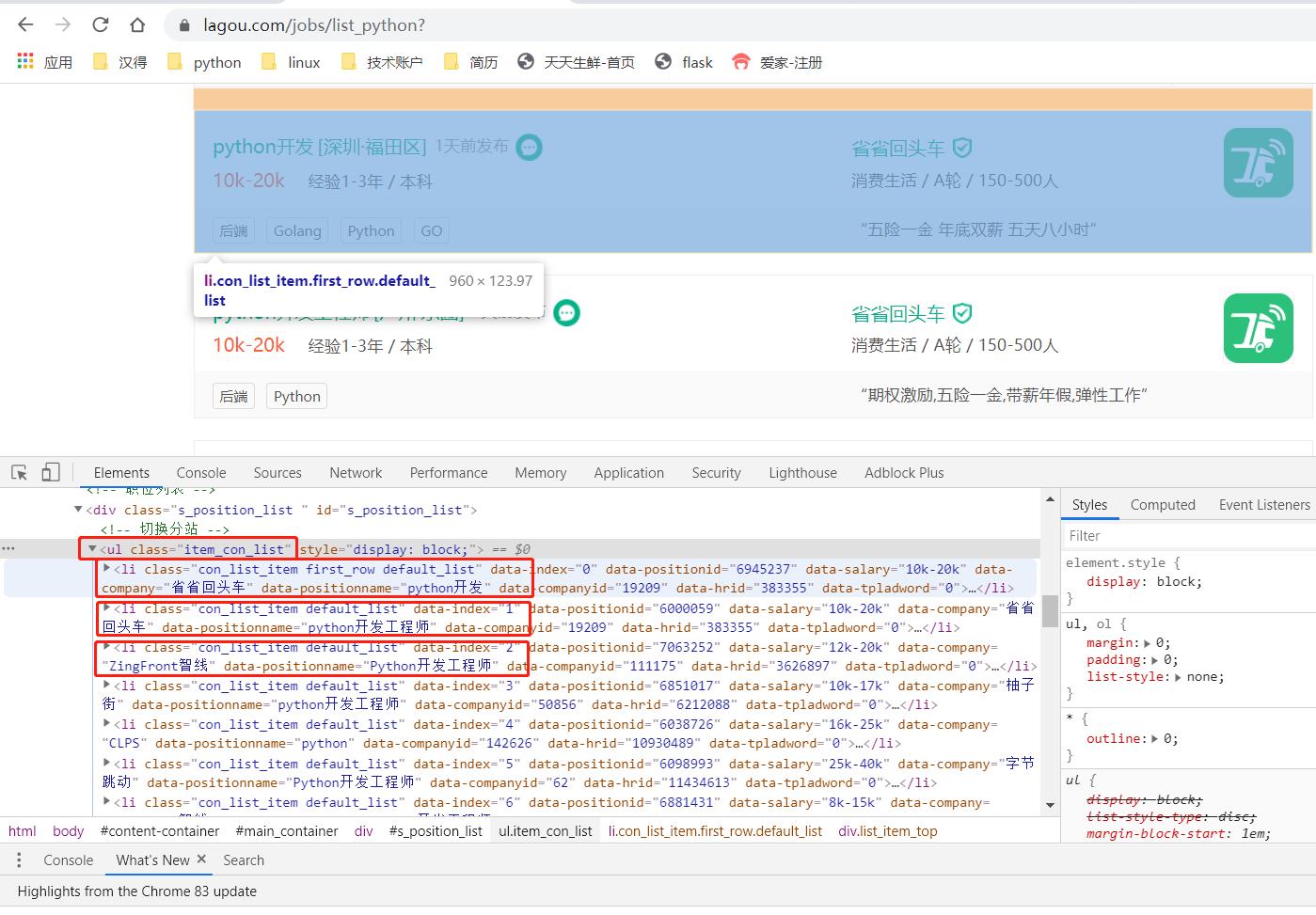
因为我们需要每个职位的具体信息, 因此需要获取到每条搜索结果的详情url, 即点击搜索结果后进入的详情页的url.
继续查看li标签中的元素, 找到想要的详情url, 找到后的url为: href=https://www.lagou.com/jobs/6945237.html?show=b6e8e778fcae4c2aa2111ba58f9ebfa0
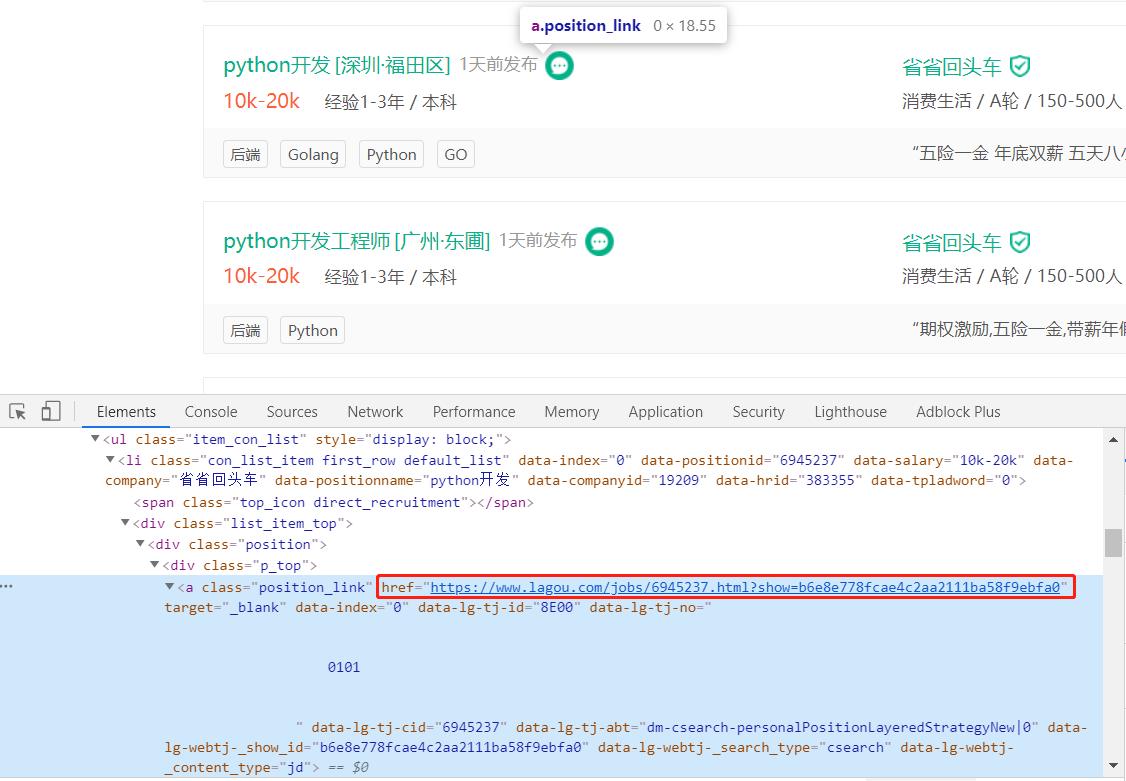
查看其它搜索结果的详情url, 发现其格式都为: href="https://www.lagou.com/jobs/{某个id}.html?show={show_id}" rel="external nofollow"
对于第一个ID, 每条结果的id都不一样, 猜想其为标记每个职位的唯一id, 对于show_id, 每条结果的id都是一样的, 尝试删除show参数, 发现一样可以访问到具体结果详情页
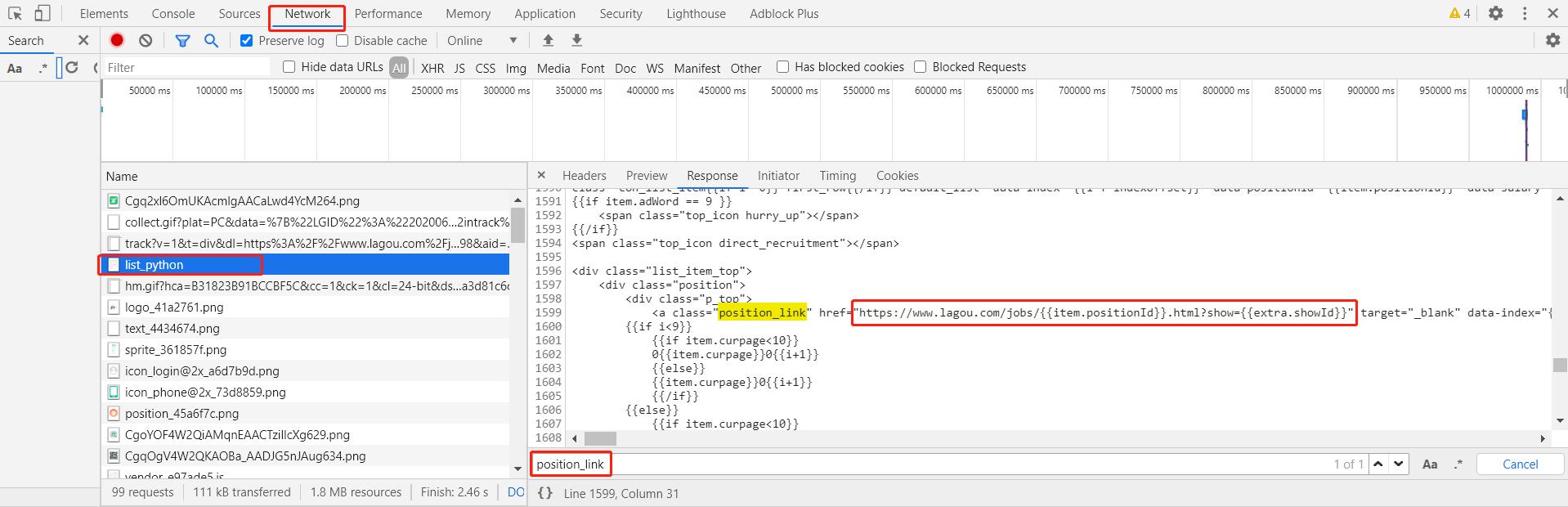
那么我们直接通过xpath提取到每个职位的第一个ID即可, 但是调试工具的elements标签下的html是最终网页展示的html, 并不一定就是我们访问 https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python 返回的response的html, 因此点到Network标签, 重新刷新一下页面, 找到 https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python 对应的请求, 查看其对应的response, 搜索 'position_link'(即前面我们在elements中找到的每条搜索结果的详情url), 发现确实返回了一个网址, 但是其重要的两个ID并不是直接放回的, 而是通过js生成的, 说明我们想要的具体数据并不是这个这个请求返回的.
那么我们就需要找到具体是那个请求会返回搜索结果的信息, 一般这种情况首先考虑是不是通过ajax获取的数据, 筛选类型为XHR(ajax)的请求, 可以逐个点开查看response, 发现 positionAjax.json 返回的数据中就存在我们想要的每条搜索结果的信息. 说明确实是通过ajax获取的数据, 其实点击下一页, 我们也可以发现地址栏url地址并没有发生变化, 只是局部刷新了搜索结果的数据, 也说明了搜索结果是通过ajax返回的.
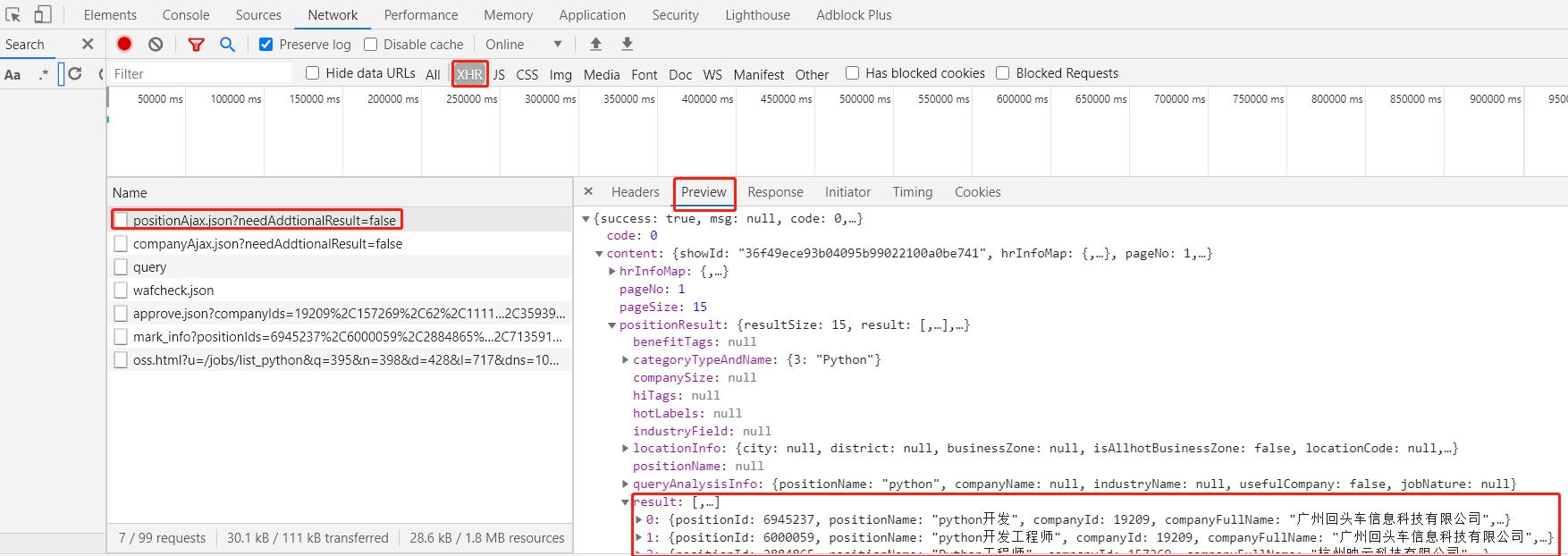
分析上面ajax的response, 查看其中是否有我们想要的职位ID, 在preview中搜索之前在elements中找到的某个职位的url的两个ID, 确实两个ID都存在response中, 分析发现第一个ID即为positionId, 第二个即为showId, 我们还可以发现response中返回了当前的页码数pageNo
因此我们只需要访问上面ajax对应的url: https://www.lagou.com/jobs/positionAjax.json?needAddtionalResult=false 就可以拿到我们想要的ID, 然后填入详情url模板: https://www.lagou.com/jobs/{position_id}.html?show={show_id}中即可访问详情页了.
但是当我们直接访问 https://www.lagou.com/jobs/positionAjax.json?needAddtionalResult=false 时 ,返回的结果却是: {"status":false,"msg":"您操作太频繁,请稍后再访问","clientIp":"139.226.66.44","state":2402}
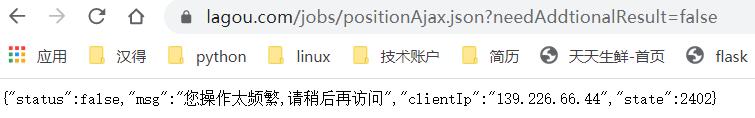
经过百度查询后发现原来直接访问上述地址是不行的, 这也是拉钩的一个反爬策略, 需要我们带上之前访问查询结果页(https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python?)的cookie才行, 因为我们这里使用的是scrapy框架, 该框架是能够自带上次请求的cookie来访问下一个请求的, 所以我们这里不需要手动去添加cookie信息, 只需要首先访问一下查询结果页就可以了. 即start_url = https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python
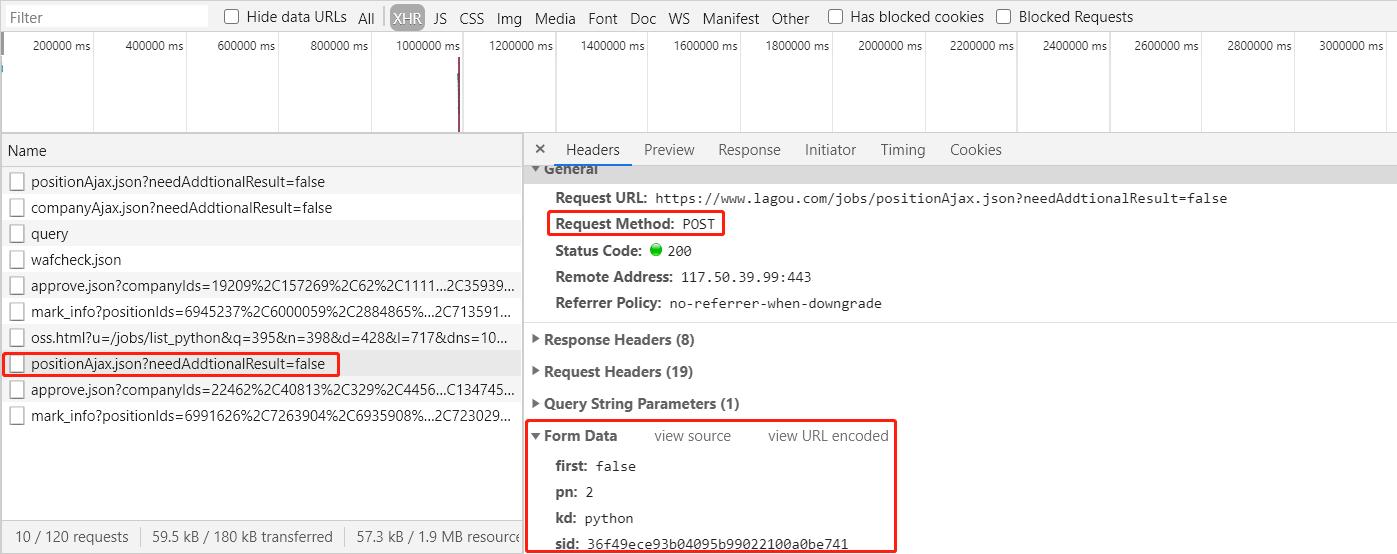
此外发现这个ajax请求是通过POST方式发送的, 因此还需要分析它提交的form数据, 在第一页中有三条数据信息, first为true, pn为1 kd为python , 第二页中first为false, pn为2, kd同样为python, 且多了一个sid
分析这四个参数, 第一个first为表示是否是第一页, 第二个pn为表示当前页码数, 第三个kd为表示搜索的关键字, 第四个sid经过和上面showId对比发现其值就为showId
分析职位详情页
前面分析完后就可以拼接出职位详情页url了, 点开详情页, 同样的思路分析我们想要的数据是不是就在详情页的url中, 这里想要职位名称, 工资, 地点, 经验, 关键字, 公司信息等

在network中查找对应的response, 发现数据确实就存在response中, 因此直接通过xpath就可以提取想要的数据了
编写爬虫代码
具体代码在github:
这里只放出关键代码
创建scrapy项目
scrapy startproject LaGou创建爬虫
scrapy genspider lagou www.lagou.com编写items.py, 设置要想爬取的字段
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define here the models for your scraped items # # See documentation in: # https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html import scrapy class LagouItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: job_url = scrapy.Field() job_name = scrapy.Field() salary = scrapy.Field() city = scrapy.Field() area = scrapy.Field() experience = scrapy.Field() education = scrapy.Field() labels = scrapy.Field() publish_date = scrapy.Field() company = scrapy.Field() company_feature = scrapy.Field() company_public = scrapy.Field() company_size= scrapy.Field() ``` <p>编写爬虫代码 lagou.py</p> ```python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy from LaGou.items import LagouItem import json from pprint import pprint import time class LagouSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 'lagou' allowed_domains = ['www.lagou.com'] start_urls = ['https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python?'] def __init__(self): # 设置头信息, 若不设置的话, 在请求第二页时即被拉勾网认为是爬虫而不能爬取数据 self.headers = { "Accept": "application/json, text/javascript, */*; q=0.01", "Connection": "keep-alive", "Host": "www.lagou.com", "Referer": 'https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_Python?', "Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8", "referer": "https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python?" } self.sid = '' self.job_url_temp = 'https://www.lagou.com/jobs/{}.html?show={}' # 清空文件 with open('jobs.json', 'w') as f: f.truncate() def parse(self, response): """ 解析起始页 """ # response为GET请求的起始页, 自动获取cookie # 提交POST带上前面返回的cookies, 访问数据结果第一页 yield scrapy.FormRequest( 'https://www.lagou.com/jobs/positionAjax.json?needAddtionalResult=false', callback=self.parse_list, formdata={"first": "false", "pn": "1", "kd": "python", }, headers=self.headers ) def parse_list(self, response): """ 解析结果列表页的json数据 """ # 获取返回的json,转为字典 res_dict = json.loads(response.text) # 判断返回是否成功 if not res_dict.get('success'): print(res_dict.get('msg', '返回异常')) else: # 获取当前页数 page_num = res_dict['content']['pageNo'] print('正在爬取第{}页'.format(page_num)) # 获取sid if not self.sid: self.sid = res_dict['content']['showId'] # 获取响应中的职位url字典 part_url_dict = res_dict['content']['hrInfoMap'] # 遍历职位字典 for key in part_url_dict: # 初始化保存职位的item item = LagouItem() # 拼接完整职位url item['job_url'] = self.job_url_temp.format(key, self.sid) # 请求职位详情页 yield scrapy.Request( item['job_url'], callback=self.parse_detail, headers=self.headers, meta={'item': item} ) # 获取下一页 if page_num < 30: # time.sleep(2) yield scrapy.FormRequest( 'https://www.lagou.com/jobs/positionAjax.json?needAddtionalResult=false', callback=self.parse_list, formdata={"first": "false", "pn": str(page_num+1), "kd": "python", "sid": self.sid }, headers=self.headers ) def parse_detail(self, response): """ 解析职位详情页 """ # 接收item item = response.meta['item'] # 解析数据 # 获取职位头div job_div = response.xpath('//div[@class="position-content-l"]') if job_div: item['job_name'] = job_div.xpath('./div/h1/text()').extract_first() item['salary'] = job_div.xpath('./dd/h3/span[1]/text()').extract_first().strip() item['city'] = job_div.xpath('./dd/h3/span[2]/text()').extract_first().strip('/').strip() item['area'] = response.xpath('//div[@class="work_addr"]/a[2]/text()').extract_first() item['experience'] = job_div.xpath('./dd/h3/span[3]/text()').extract_first().strip('/').strip() item['education'] = job_div.xpath('./dd/h3/span[4]/text()').extract_first().strip('/').strip() item['labels'] = response.xpath('//ul[@class="position-label clearfix"]/li/text()').extract() item['publish_date'] = response.xpath('//p[@class="publish_time"]/text()').extract_first() item['publish_date'] = item['publish_date'].split('&')[0] # 获取公司dl company_div = response.xpath('//dl[@class="job_company"]') item['company'] = company_div.xpath('./dt/a/img/@alt').extract_first() item['company_feature'] = company_div.xpath('./dd//li[1]/h4[@class="c_feature_name"]/text()').extract_first() item['company_feature'] = item['company_feature'].split(',') item['company_public'] = company_div.xpath('./dd//li[2]/h4[@class="c_feature_name"]/text()').extract_first() item['company_size'] = company_div.xpath('./dd//li[4]/h4[@class="c_feature_name"]/text()').extract_first() yield item``` <p>编写middlewares.py, 自定义downloadermiddleware, 用来每次发送请求前, 随机设置user-agent, 这里使用了第三方库 fake_useragent, 能够随机提供user-agent, 使用前先安装: pip install fake_useragent</p> ```python from fake_useragent import UserAgent import random class RandomUserAgentDM: """ 随机获取userAgent """ def __init__(self): self.user_agent = UserAgent() def process_request(self, request, spider): request.headers['User-Agent'] = self.user_agent.random编写pipelines.py, 将数据存为json文件
import json class LagouPipeline: def process_item(self, item, spider): with open('jobs.json', 'a', encoding='utf-8') as f: item_json = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False, indent=2) f.write(item_json) f.write('\n')编写settings.py
# 设置日志显示 LOG_LEVEL = 'WARNING' # 设置ROBOTSTXT协议, 若为true则不能爬取数据 ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False # 设置下载器延迟, 反爬虫的一种策略 DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 0.25 # 开启DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = { # 'LaGou.middlewares.LagouDownloaderMiddleware': 543, 'LaGou.middlewares.RandomUserAgentDM' :100, } # 开启ITEM_PIPELINES ITEM_PIPELINES = { 'LaGou.pipelines.LagouPipeline': 300, }启动爬虫
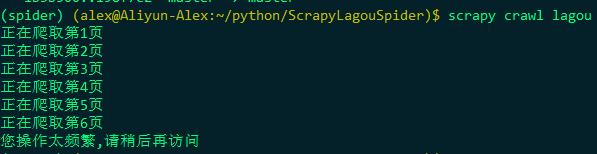
scrapy crawl lagou
发现依然只能5 6页, 说明拉勾网的反爬确实做得比较好, 还可以继续通过使用代理来进行反反爬, 这里就不再演示了,
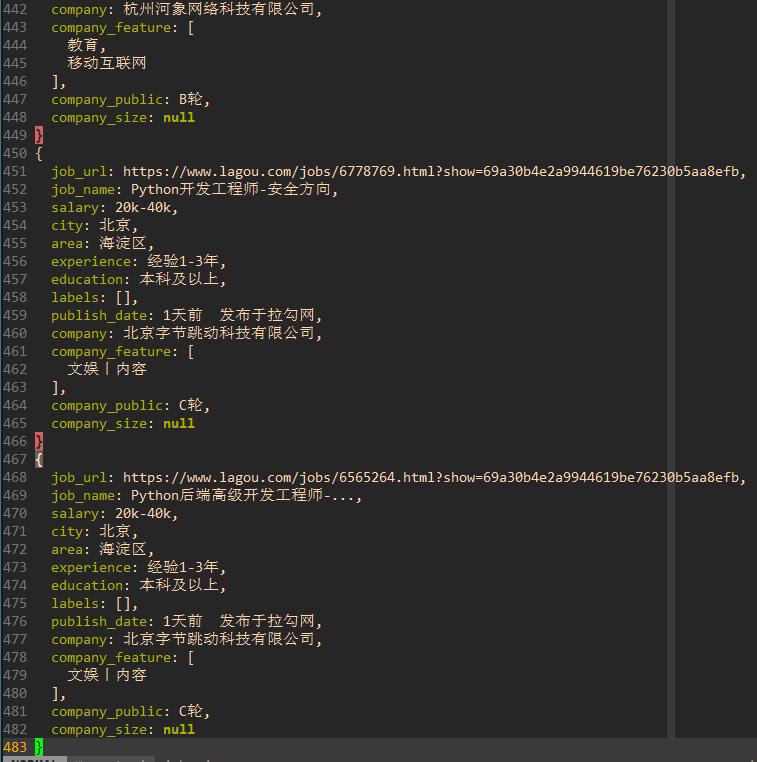
查看爬取结果
以上就是Python爬虫实例——scrapy框架爬取拉勾网招聘信息的详细内容,更多关于Python爬虫爬取招聘信息的资料请关注python博客其它相关文章!
-
<< 上一篇 下一篇 >>
标签:scrapy
Python爬虫实例——scrapy框架爬取拉勾网招聘信息
看: 1580次 时间:2020-08-26 分类 : python爬虫
- 相关文章
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫基础之爬虫的分类知识总结
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫基础讲解之请求
- 2021-07-20PyQt5爬取12306车票信息程序的实现
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫之m3u8文件里提取小视频的正确姿势
- 2021-07-20如何用python抓取B站数据
- 2021-07-20快速搭建python爬虫管理平台
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫之获取心知天气API实时天气数据并弹窗提醒
- 2021-07-20Python爬虫之批量下载喜马拉雅音频
- 2021-07-20python使用pywinauto驱动微信客户端实现公众号爬虫
- 2021-07-20Requests什么的通通爬不了的Python超强反爬虫方案!
-
搜索
-
-
推荐资源
-
Powered By python教程网 鲁ICP备18013710号
python博客 - 小白学python最友好的网站!