本文实例为大家分享了python实现梯度下降法的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
使用工具:Python(x,y) 2.6.6
运行环境:Windows10问题:求解y=2*x1+x2+3,即使用梯度下降法求解y=a*x1+b*x2+c中参数a,b,c的最优值(监督学习)
训练数据:
x_train=[1, 2], [2, 1],[2, 3], [3, 5], [1,3], [4, 2], [7, 3], [4, 5], [11, 3], [8, 7]
y_train=[7, 8, 10, 14, 8, 13, 20, 16, 28,26]
测试数据:
x_test = [1, 4],[2, 2],[2, 5],[5, 3],[1,5],[4, 1]
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Wed Nov 16 09:37:03 2016 @author: Jason """ import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # y=2 * (x1) + (x2) + 3 rate = 0.001 x_train = np.array([[1, 2], [2, 1],[2, 3], [3, 5], [1, 3], [4, 2], [7, 3], [4, 5], [11, 3], [8, 7] ]) y_train = np.array([7, 8, 10, 14, 8, 13, 20, 16, 28, 26]) x_test = np.array([[1, 4],[2, 2],[2, 5],[5, 3],[1, 5],[4, 1]]) a = np.random.normal() b = np.random.normal() c = np.random.normal() def h(x): return a*x[0]+b*x[1]+c for i in range(100): sum_a=0 sum_b=0 sum_c=0 for x, y in zip(x_train, y_train): for xi in x: sum_a = sum_a+ rate*(y-h(x))*xi sum_b = sum_b+ rate*(y-h(x))*xi #sum_c = sum_c + rate*(y-h(x)) *1 a = a + sum_a b = b + sum_b c = c + sum_c plt.plot([h(xi) for xi in x_test]) print(a) print(b) print(c) result=[h(xi) for xi in x_train] print(result) result=[h(xi) for xi in x_test] print(result) plt.show()运行结果:
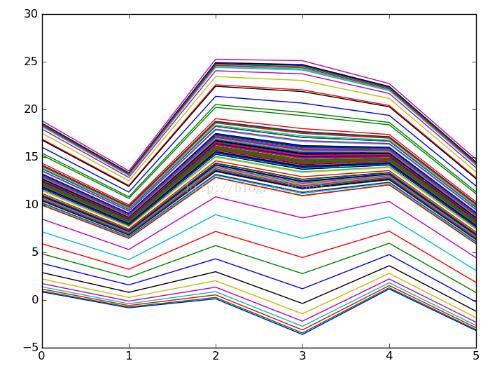
结论:线段是在逐渐逼近的,训练数据越多,迭代次数越多就越逼近真实值。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持python博客。
-
<< 上一篇 下一篇 >>
标签:numpy matplotlib
python实现梯度下降法
看: 1308次 时间:2020-07-30 分类 : python教程
- 相关文章
- 2021-12-20Python 实现图片色彩转换案例
- 2021-12-20python初学定义函数
- 2021-12-20图文详解Python如何导入自己编写的py文件
- 2021-12-20python二分法查找实例代码
- 2021-12-20Pyinstaller打包工具的使用以及避坑
- 2021-12-20Facebook开源一站式服务python时序利器Kats详解
- 2021-12-20pyCaret效率倍增开源低代码的python机器学习工具
- 2021-12-20python机器学习使数据更鲜活的可视化工具Pandas_Alive
- 2021-12-20python读写文件with open的介绍
- 2021-12-20Python生成任意波形并存为txt的实现
-
搜索
-
-
推荐资源
-
Powered By python教程网 鲁ICP备18013710号
python博客 - 小白学python最友好的网站!